500 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
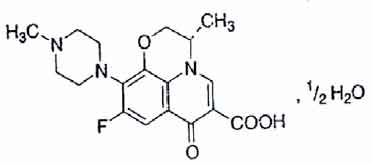
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS (Levofloxacin) is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Levofloxacin, a chiral fluorinated carboxyquinolone, is the pure (-)-(S)-enantiomer of the racemic drug substance ofloxacin. Chemically, Levofloxacin is (-)-(S)-9-Fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de]1, 4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid, hemihydrate. The molecular formula is C18H20FN3O4 • ½ H2O and the molecular weight is 370.38.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
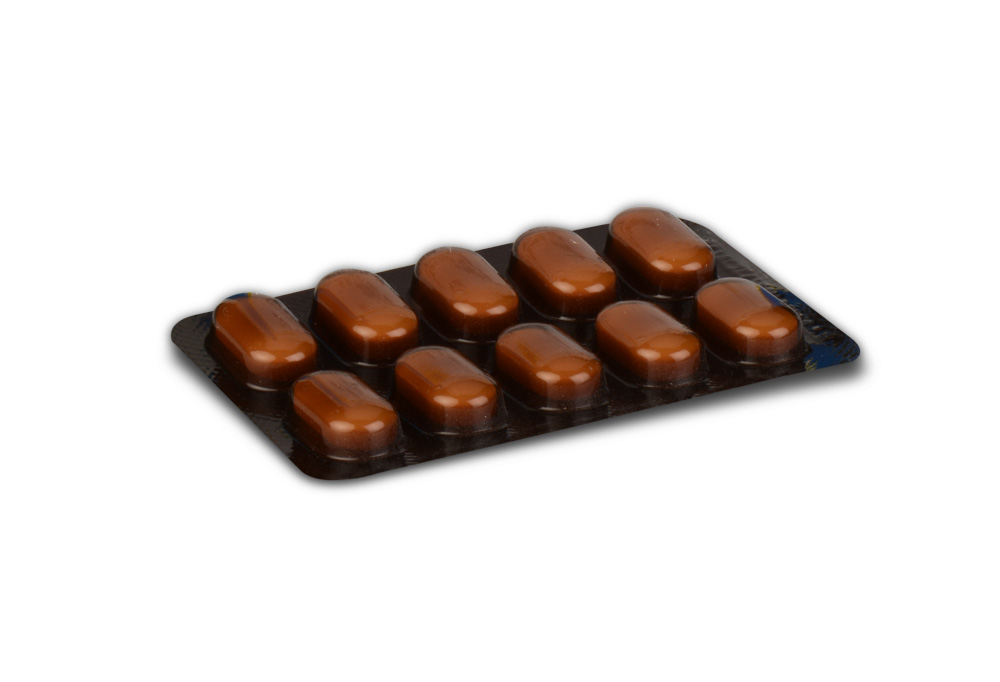
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are brown coloured, elongated, biconvex, film coated tablets having breakline on one side & plain on other side.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Levofloxacin (anhydrous) USP 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colours : Red Ferric Oxide NF, Titanium Dioxide B.P.
Administration :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are for oral use.
Method of Administration :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS should be swallowed without crushing and with sufficient amount of liquid. They may be divided at the score line to adapt the dose. The tablets may be taken during meals or between meals. LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS should be taken at least two hours before or after iron salts, zinc salts, magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids, or didanosine (only didanosine formulations with aluminium or magnesium containing buffering agents), and sucralfate administration, since reduction of absorption can occur.
Dosage :
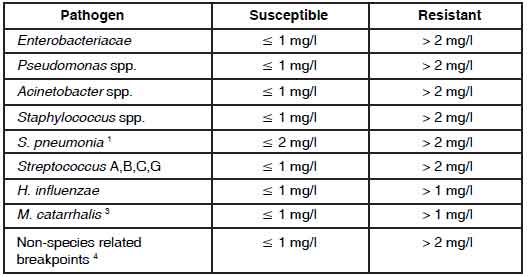
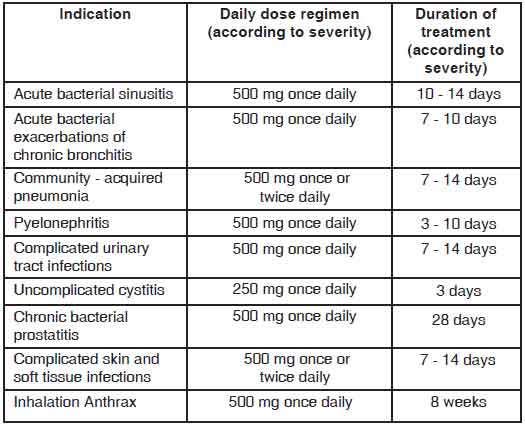
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are administered once or twice daily. The dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection and the susceptibility of the presumed causative pathogen. LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS may also be used to complete a course of therapy in patients who have shown improvement during initial treatment with intravenous levofloxacin ; given the bioequivalence of the parenteral and oral forms, the same dosage can be used. The following dose recommendations can be given for LEVOFLOXACIN
TABLETS :
Dosage in patients with normal renal function :
(creatinine clearance > 50 ml/min)
Impaired liver function :
No adjustment of dose is required since levofloxacin is not metabolised to any relevant extent by the liver and is mainly excreted by the kidneys.
Elderly population :
No adjustment of dose is required in the elderly, other than that imposed by consideration of renal function.
Paediatric population :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS is contraindicated in children and growing adolescents.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are contraindicated in :
• patients hypersensitive to levofloxacin or other quinolones or any of the excipients.
• patients with epilepsy.
• patients with history of tendon disorders related to fluoroquinolone administration.
• children or growing adolescents.
• during pregnancy.
• breast-feeding women.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
In the most severe cases of pneumococcal pneumonia LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS may not be the optimal therapy. Nosocomial infections due to P. aeruginosa may require combination therapy.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) :
Levofloxacin is not effective against infections caused by MRSA. In infections suspicious for MRSA levofloxacin should be combined with an agent approved to treat MRSA infections.
Tendinitis and tendon rupture :
Tendinitis may rarely occur. It most frequently involves the Achilles tendon and may lead to tendon rupture. The risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture is increased in the elderly and in patients using corticosteroids. Close monitoring of these patients is therefore necessary if they are prescribed LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS All patients should consult their physician if they experience symptoms of tendinitis. If tendinitis is suspected, treatment with LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS must be halted immediately, and appropriate treatment (e.g. immobilisation) must be initiated for the affected tendon.
Clostridium difficile-associated disease :
Diarrhoea, particularly if severe, persistent and/or bloody, during or after treatment with LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS, may be symptomatic of Clostridium difficile - associated disease, the most severe form of which is pseudomembranous enterocolitis. If pseudomembranous enterocolitis is suspected, LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS must be stopped immediately and patients should be treated with supportive measures and specific therapy without delay (e.g. oral metronidazole or vancomycin). Products inhibiting the peristalsis are contraindicated in this clinical situation.
Patients predisposed to seizures :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are contraindicated in patients with a history of epilepsy and, as with other quinolones, should be used with extreme caution in patients predisposed to seizures, such as patients with pre-existing central nervous system damage; concomitant treatment with fenbufen and similar non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or with drugs which lower the cerebral seizure threshold, such as theophylline. In case of convulsive seizures, treatment with levofloxacin should be discontinued.
Patients with G-6- phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency :
Patients with latent or actual defects in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity may be prone to haemolytic reactions when treated with quinolone antibacterial agents, and so levofloxacin should be used with caution.
Patients with renal impairment :
Since levofloxacin is excreted mainly by the kidneys, the dose of LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.
Hypersensitivity reactions :
Levofloxacin can cause serious, potentially fatal hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. angioedema to anaphylactic shock), occasionally following the initial dose. Patients should discontinue treatment immediately and contact their physician or an emergency physician, who will initiate appropriate emergency measures.
Hypoglycaemia :
As with all quinolones, hypoglycaemia has been reported, usually in diabetic patients receiving concomitant treatment with an oral hypoglycaemic agent (e.g. glibenclamide) or with insulin. In these diabetic patients, careful monitoring of blood glucose is recommended.
Prevention of photosensitization :
Although photosensitisation is very rare with levofloxacin, it is recommended that patients should not expose themselves unnecessarily to strong sunlight or to artificial UV rays (e.g. sunray lamp, solarium), in order to prevent photosensitization.
Patients treated with Vitamin K antagonists :
Due to possible increase in coagulation tests (PT/INR) and/or bleeding in patients treated with levofloxacin in combination with a vitamin K antagonist (e.g. warfarin), coagulation tests should be monitored when these drugs are given concomitantly.
Psychotic reactions :
Psychotic reactions have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including levofloxacin. In very rare cases these have progressed to suicidal thoughts and self-endangering behaviour- sometimes after only a single dose of levofloxacin. In the event that the patient develops these reactions, levofloxacin should be discontinued and appropriate measures instituted. Caution is recommended if levofloxacin is to be used in psychotic patients or in patients with a history of psychiatric disease.
Cardiac disorders :
Caution should be taken when using fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin, in patients with known risk factors for prolongation of the QT interval such as, for example :
- congenital long QT syndrome
- concomitant use of drugs that are known to prolong the QT interval (e.g. Class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides).
- uncorrected electrolyte imbalance (e.g. hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia)
- elderly
- cardiac disease (e.g. heart failure, myocardial infarction, bradycardia)
Peripheral neuropathy :
Sensory or sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy has been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones, including levofloxacin, which can be rapid in its onset. Levofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition.
Opiates :
In patients treated with levofloxacin, determination of opiates in urine may give false-positive results. It may be necessary to confirm positive opiate screens by a more specific method.
Hepatobiliary disorders :
Cases of hepatic necrosis up to life threatening hepatic failure have been reported with levofloxacin, primarily in patients with severe underlying diseases, e.g. sepsis. Patients should be advised to stop treatment and contact their doctor if signs and symptoms of hepatic disease develop such as anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, pruritus or tender abdomen.
Pregnancy : Category C
There are limited data from the use of levofloxacin in pregnant women. Animal studies do not indicate direct or indirect harmful effects with respect to reproductive toxicity. However in the absence of human data and due to experimental data suggesting a risk of damage to the weight - bearing cartilage of the growing organism by fluoroquinolones, levofloxacin should only be used in pregnancy if the benefit is considered to outweigh the risks, and there are no available treatment alternatives.
Nursing Mothers :
Levofloxacin is contraindicated in breast - feeding women. There is insufficient information on the excretion of levofloxacin in human milk ; however other fluoroquinolones are excreted in breast milk. In the absence of human data and due to experimental data suggesting a risk of damage to the weight-bearing cartilage of the growing organism by fluoroquinolones, LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS must not be used in breast-feeding women.
Paediatric Use :
Quinolones, including levofloxacin, cause arthropathy and osteochondrosis in juvenile animals of several species.
Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure) :
Levofloxacin is indicated in paediatric patients for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure). The risk-benefit assessment indicates that administration of levofloxacin to paediatric patients is appropriate. The safety of levofloxacin in paediatric patients treated for more than 14 days has not been studied. The pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin following a single intravenous dose were investigated in paediatric patients ranging in age from six months to 16 years. Paediatric patients cleared levofloxacin faster than adult patients resulting in lower plasma exposures than adults for a given mg/kg dose.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Effect of other medicinal products on levofloxacin.
Iron salts, magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids :
Levofloxacin absorption is significantly reduced when iron salts, or magnesium- or aluminium-containing antacids are administered concomitantly. It is recommended that preparations containing divalent or trivalent cations such as iron salts, or magnesium-or aluminium-containing antacids should not be taken 2 hours before or after LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS administration. No interaction was found with calcium carbonate.
Sucralfate :
The bioavailability of LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS is significantly reduced when administered together with sucralfate. If the patient is to receive both sucralfate and LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS, it is best to administer sucralfate 2 hours after the LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS administration.
Theophylline, fenbufen or similar non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs :
No pharmacokinetic interactions of levofloxacin were found with theophylline in a clinical study. However a pronounced lowering of the cerebral seizure threshold may occur when quinolones are given concurrently with theophylline, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or other agents which lower the seizure threshold. Levofloxacin concentrations were about 13 % higher in the presence of fenbufen than when administered alone.
Probenecid and cimetidine :
Probenecid and cimetidine had a statistically significant effect on the elimination of levofloxacin. The renal clearance of levofloxacin was reduced by cimetidine (24 %) and probenecid (34 %). This is because both drugs are capable of blocking the renal tubular secretion of levofloxacin. However, at the tested doses in the study, the statistically significant kinetic differences are unlikely to be of clinical relevance. Caution should be exercised when levofloxacin is coadministered with drugs that effect the tubular renal secretion such as probenecid and cimetidine, especially in renally impaired patients.
Effect of levofloxacin on other medicinal products :
Ciclosporin :
The half-life of ciclosporin was increased by 33 % when coadministered with levofloxacin.
Vitamin K antagonists :
Increased coagulation tests (PT/INR) and/or bleeding, which may be severe, have been reported in patients treated with levofloxacin in combination with a vitamin K antagonist (e.g. warfarin). Coagulation tests, therefore, should be monitored in patients treated with vitamin K antagonists.
Drugs known to prolong the QT interval :
Levofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g. Class IA and III antiarrhythmics, tricyclic antidepressants, macrolides, antipsychotic).
SIDE EFFECTS :
Side effects are listed below by system organ class and frequency.
Frequencies are defined using the following convention :
Very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100, < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000, < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000, < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data). Within each frequency grouping, side effects are presented in order of decreasing seriousness.
Cardiac disorders : Rare : Tachycardia
Not Known : Ventricular arrhythmia and torsades de pointes (reported predominantly in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation), Electrocardiogram QT prolonged.
OVERDOSAGE :
According to toxicity studies in animals or clinical pharmacology studies performed with supra-therapeutic doses, the most important signs to be expected following acute overdose of LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS are central nervous system symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, impairment of consciousness and convulsive seizures, increases in QT interval as well as gastro-intestinal reactions such as nausea and mucosal erosions. CNS effects including confusional state, convulsion, hallucination, and tremor have been observed in post marketing experience.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be implemented. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation. Antacids may be used for protection of gastric mucosa. Haemodialysis, including peritoneal dialysis and CAPD, are not effective in removing levofloxacin from the body. No specific antidote exists.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C, protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
LEVOFLOXACIN TABLETS contains Levofloxacin (anhydrous) USP 500 mg.
1 Blister of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular