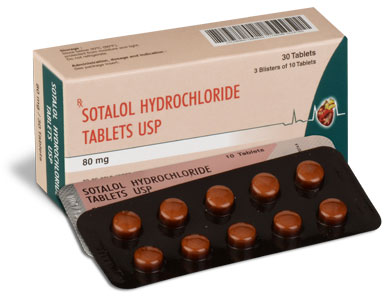
80 mg, 160 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
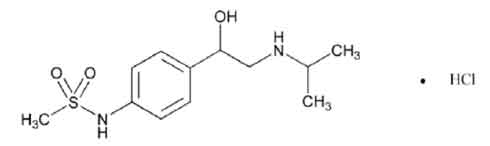
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP (Sotalol Hydrochloride) is a non-cardioselective beta blocker. Chemically, Sotalol Hydrochloride is Methanesulfonamide, N-[4-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl)amino]ethyl]phenyl]-,monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C12H20N2O3S.HCl and molecular weight is 308.83.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
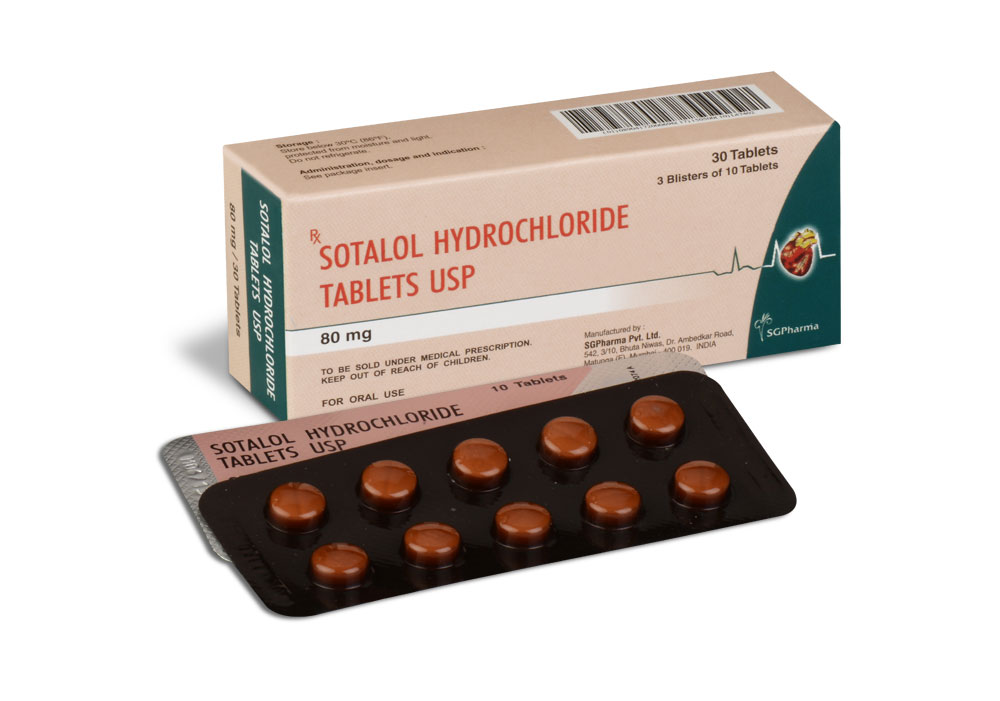
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP 80 mg are white coloured, circular biconvex uncoated Tablets with breakline on one side and SGP embossed on other side.
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP 160 mg are white coloured, circular biconvex uncoated Tablets with breakline on one side.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Sotalol Hydrochloride USP 80 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Sotalol Hydrochloride USP 160 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Sotalol is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker without sympathomimetic activity or membrane stabilising activity. It causes a decrease in heart rate and a limited reduction in the force of contraction of the heart. There is a reduction in cardiac work and in myocardial oxygen demand. Sotalol does not decrease blood pressure in normotensive subjects. Sotalol also possesses class III antiarrhythmic activity. Sotalol has no known effect on the upstroke velocity of the action potential, therefore no known effect on the
depolarisation phase. Its major effects are prolongation of the atrial, ventricular and accessory pathway effective refractory periods. The effect on the ventricular myocardium may be reflected by a lengthening of the QTc interval on electrocardiographic recordings. Like most other beta-blockers, sotalol inhibits renin release. This suppressive effect is significant both at rest and during exercise.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Sotalol is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and peak plasma concentrations are obtained about 2 to 4 hours after a dose. The plasma elimination half-life is about10 to 20 hours. Sotalol has low lipid solubility. Very little is metabolised and it is excreted unchanged in the urine. Binding to plasma proteins is reported to be low. It crosses the placenta and is distributed into breast milk; concentrations in milk may be higher than those in maternal serum. Only small amounts are reported to cross the blood-brain barrier and enter the CSF. Sotalol is removed by dialysis.
INDICATIONS :
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP indicated for :
Ventricular arrhythmias :
Treatment of life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias ; Treatment of symptomatic non-sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmias;
Supraventricular arrhythmias :
Prophylaxis of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal A-V nodal re-entrant tachycardia, paroxysmal A-V re-entrant tachycardia using accessory pathways, and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia after cardiac surgery;
Maintenance of normal sinus rhythm following conversion of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
Administration :
For oral use. SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be taken preferably 1-2 hours before meal.
Dosage :
The initiation of treatment or changes in dosage with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should follow an appropriate medical evaluation including ECG control with measurement of the corrected QT interval, and assessment of renal function, electrolyte balance, and concomitant medications. As with other antiarrhythmic agents, it is recommended that SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP be initiated and doses increased in a facility capable of monitoring and assessing cardiac rhythm. The dosage must be individualized and based on the patient’s response. Proarrhythmic events can occur not only at initiation of therapy, but also with each upward dosage adjustment. In view of its β-adrenergic blocking properties, treatment with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should not be discontinued suddenly, especially in patients with ischaemic heart disease (angina pectoris, prior acute myocardial infarction) or hypertension, to prevent exacerbation of the disease.
The following dosing schedule can be recommended :
The initial dose is 80 mg, administered either singly or as two divided doses. Oral dosage of SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be adjusted gradually allowing 2-3 days between dosing increments in order to attain steady-state, and to allow monitoring of QT intervals. Most patients respond to a daily dose of 160 to 320 mg administered in two divided doses at approximately 12 hour intervals. Some patients with life-threatening refractory ventricular arrhythmias may require doses as high as 480 - 640 mg/day. These doses should be used under specialist supervision and should only be prescribed when the potential benefit outweighs the increased risk of adverse events, particularly proarrhythmias.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should not be used where there is evidence of sick sinus syndrome; second and third degree AV heart block unless a functioning pacemaker is present; congenital or acquired long QT syndromes; torsades de pointes; symptomatic sinus bradycardia; uncontrolled congestive heart failure; cardiogenic shock; anaesthesia that produces myocardial depression; untreated phaeochromocytoma; hypotension (except due to arrhythmia); Reynard’s phenomenon and severe peripheral circulatory disturbances; history of chronic obstructive airway disease or bronchial asthma (a warning will appear on the label); hypersensitivity to any of the components of the formulation; metabolic acidosis; renal failure (creatinine clearance < 10 ml/min). SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
Abrupt Withdrawal : Hypersensitivity to catecholamines is observed in patients withdrawn from beta-blocker therapy. Occasional cases of exacerbation of angina pectoris, arrhythmias, and in some cases, myocardial infarction have been reported after abrupt discontinuation of therapy. Patients should be carefully monitored when discontinuing chronically administered SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP, particularly those with ischaemic heart disease. If possible the dosage should be gradually reduced over a period of one to two weeks, if necessary at the same time initiating replacement therapy. Abrupt discontinuation may unmask latent coronary insufficiency. In addition, hypertension may develop. Proarrhythmia : The most dangerous adverse effect of Class I and Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (such as sotalol) is the aggravation of pre-existing arrhythmias or the provocation of new arrhythmias. Drugs that prolong the QT-interval may cause torsades de pointes, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with prolongation of the QT-interval. Experience to date indicates that the risk of torsades de pointes is associated with the prolongation of the QT-interval, reduction of the heart rate, reduction in serum potassium and magnesium, high plasma sotalol concentrations and with the concomitant use of sotalol and other medications which have been associated with torsades de pointes. Females may be at increased risk of developing torsades de pointes.
The incidence of torsades de pointes is dose dependent. Torsades de pointes usually occur within 7 days of initiating therapy or escalation of the dose and can progress to ventricular fibrillation. In clinical trials of patients with sustained VT/VF the incidence of severe proarrhythmia (torsades de pointes or new sustained VT/VF) was < 2 % at doses up to 320 mg. The incidence more than doubled at higher doses. Other risk factors for torsades de pointes were excessive prolongation of the QTC and history of cardiomegaly or congestive heart failure. Patients with sustained ventricular tachycardia and a history of congestive heart failure have the highest risk of serious proarrhythmia (7 %). Proarrhythmic events must be anticipated not only on initiating therapy but with every upward dose adjustment. Initiating therapy at 80 mg with gradual upward dose titration thereafter reduces the risk of proarrhythmia. In patients already receiving SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP caution should be used if the QTC exceeds 500 msec whilst on therapy, and serious consideration should be given to reducing the dose or discontinuing therapy when the QTC- interval exceeds 550 msec. Due to the multiple risk factors associated with torsades de pointes, however, caution should be exercised regardless of the QTC-interval.
Electrocardiographic Changes : Excessive prolongation of the QT-interval > 500 msec, can be a sign of toxicity and should be avoided (see Proarrhythmias above). Sinus bradycardia has been observed very commonly in arrhythmia patients receiving sotalol in clinical trials. Bradycardia increases the risk of torsades de pointes. Sinus pause, sinus arrest and sinus node dysfunction occur in less than 1 % of patients. The incidence of 2nd- or 3rd-degree AV block is approximately 1 %.
Anaphylaxis : Patients with a history of anaphylactic reaction to a variety of allergens may have a more severe reaction on repeated challenge while taking beta-blockers. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of adrenaline used to treat the allergic reaction.
Anaesthesia : As with other beta-blocking agents, SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be used with caution in patients undergoing surgery and in association with anaesthetics that cause myocardial depression, such as cyclopropane or trichloroethylene.
Diabetes Mellitus : SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be used with caution in patients with diabetes (especially labile diabetes) or with a history of episodes of spontaneous hypoglycaemia, since beta-blockade may mask some important signs of the onset of acute hypoglycaemia, e.g. tachycardia.
Thyrotoxicosis : Beta-blockade may mask certain clinical signs of hyperthyroidism (e.g., tachycardia). Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockade which might be followed by an exacerbation of symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including thyroid storm.
Renal Impairment : As sotalol is mainly eliminated via the kidneys the dose should be adjusted in patients with renal impairment.
Psoriasis : Beta-blocking drugs have been reported rarely to exacerbate the symptoms of psoriasis vulgaris. This product contains lactose, patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp-lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicinal product.
Pregnancy : Category B
Animal studies with sotalol hydrochloride have shown no evidence of teratogenicity or other harmful effects on the foetus. Although there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women, sotalol hydrochloride has been shown to cross the placenta and is found in amniotic fluid. Beta-blockers reduce placental perfusion, which may result in intrauterine foetal death, immature and premature deliveries. In addition, adverse effects (especially hypoglycaemia and bradycardia) may occur in foetus and neonate. There is an increased risk of cardiac and pulmonary complications in the neonate in the postnatal period. Therefore, SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefits outweigh the possible risk to the foetus. The neonate should be monitored very carefully for 48 - 72 hours after delivery if it was not possible to interrupt maternal therapy with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP 2-3 days before the birthdate.
Lactation :
Most beta-blockers, particularly lipophilic compounds, will pass into breast milk although to a variable extent. Breast feeding is therefore not recommended during administration of these compounds.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
There are no data available, but the occasional occurrence of side-effects such as dizziness and fatigue should be taken into account.
INTERACTIONS :
Antiarrhythmics Class : 1a antiarrhythmic drugs, such as disopyramide, quinidine and procainamide and other antiarrhythmic drugs such as amiodarone and bepridil are not recommended as concomitant therapy with sotalol, because of their potential to prolong refractoriness. The concomitant use of other beta-blocking agents with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP may result in additive Class II effects.
Other drugs prolonging the QT-interval : sotalol should be given with extreme caution in conjunction with other drugs known to prolong the QT-interval such as phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, terfenadine and astemizole. Other drugs that have been associated with an increased risk for torsades de pointes include erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, and quinolone antibiotics.
Floctafenine : beta-adrenergic blocking agents may impede the compensatory cardiovascular reactions associated with hypotension or shock that may be induced by Floctafenine.
Calcium channel blocking drugs : Concurrent administration of beta-blocking agents and calcium channel blockers has resulted in hypotension, bradycardia, conduction defects, and cardiac failure. Beta-blockers should be avoided in combination with cardiodepressant calcium-channel blockers such as verapamil and diltiazem because of the additive effects on atrioventricular conduction, and ventricular function.
Potassium-Depleting Diuretic : Hypokalaemia or hypomagnesaemia may occur, increasing the potential for torsade de pointes.
Other potassium-depleting drugs : Amphotericin B (IV route), corticosteroids (systemic administration), and some laxatives may also be associated with hypokalaemia; potassium levels should be monitored and corrected appropriately during concomitant administration with sotalol.
Clonidine : Beta-blocking drugs may potentiate the rebound hypertension sometimes observed after discontinuation of clonidine; therefore, the beta-blocker should be discontinued slowly several days before the gradual withdrawal of clonidine.
Digitalis glycosides : Single and multiple doses of sotalol do not significantly affect serum digoxin levels. Proarrhythmic events were more common in sotalol treated patients also receiving digitalis glycosides; however, this may be related to the presence of CHF, a known risk factor for proarrhythmia, in patients receiving digitalis glycosides. Association of digitalis glycosides with beta-blockers may increase auriculo-ventricular conduction time.
Catecholamine-depleting agents : Concomitant use of catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine, guanethidine, or alpha methyldopa, with a beta-blocker may produce an excessive reduction of resting sympathetic nervous tone. Patients should be closely monitored for evidence of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia which may produce syncope.
Insulin and oral hypoglycaemics : Hyperglycaemia may occur, and the dosage of antidiabetic drugs may require adjustment. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia (tachycardia) may be masked by beta-blocking agents.
Neuromuscular blocking agents : Like Tubocurarin The neuromuscular blockade is prolonged by beta-blocking agents.
Beta-2-receptor stimulants : Patients in need of beta-agonists should not normally receive SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP. However, if concomitant therapy is necessary beta-agonists may have to be administered in increased dosages.
Drug/Laboratory interaction : The presence of SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP in the urine may result in falsely elevated levels of urinary metanephrine when measured by photometric methods. Patients suspected of having phaeochromocytoma and who are treated with sotalol should have their urine screened utilizing the HPLC assay with solid phase extraction.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The most frequent adverse effects of Sotalol arise from its beta blockade properties. Adverse effects are usually transient in nature and rarely necessitate interruption of, or withdrawal from treatment. If they do occur, they usually disappear when the dosage is reduced. The most significant adverse effects reported are proarrhythmias, including torsades de pointes. Other commonly observed side effects include fatigue, bradycardia, dyspnoea, asthenia, hypotension, edema, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dyspepsia, headache and mood changes.
OVERDOSAGE :
Intentional or accidental overdosage with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP has rarely resulted in death. Haemodialysis results in a large reduction of plasma levels of sotalol.
Signs and symptoms :
The most common signs to be expected are bradycardia, congestive heart failure, hypotension, bronchospasm and hypoglycaemia. In cases of massive intentional overdosage (2-16 gm) of SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP the following clinical findings were seen: hypotension, bradycardia, prolongation of QT-interval, premature ventricular complexes, ventricular tachycardia, torsades de pointes.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
If overdosage occurs, therapy with SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be discontinued and the patient observed closely. In addition, if required, the following therapeutic measures are suggested :
Bradycardia Atropine : (0.5 to 2 mg IV), another anticholinergic drug, a beta-adrenergic agonist (isoprenaline, 5 microgram per minute, up to 25 microgram, by slow IV injection) or transvenous cardiac pacing.
Heart Block (second and third degree) : Transvenous cardiac pacing.
Hypotension : Adrenaline rather than isoprenaline or noradrenaline may be useful, depending on associated factors.
Bronchospasm : Aminophylline or aerosol beta-2-receptor stimulant. Torsades de pointes DC cardioversion, transvenous cardiac pacing, adrenaline, and/or magnesium sulphate.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP contain Sotalol Hydrochloride USP 80 mg.
3 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
SOTALOL HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP contain Sotalol Hydrochloride USP 160 mg.
3 Strips of 10 Tablets per Box.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular