50 mg/5 ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
Protide (Protamine Sulphate) consists of the sulphates of basic peptides extracted from the sperm or roe of fish, usually species of Salmonidae and Clupeidae. It binds with heparin in solution, inhibiting its anticoagulant activity. Protamines are simple proteins of low molecular weight that are rich in arginine and strongly basic. It is a heparin antagonist. It is also a weak anticoagulant.
Protide is a clear, colourless solution filled in flint vial / ampoule of suitable size.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Protamine Sulphate I.P. 10 mg
Water for Injections I.P. q.s.
Contains no preservatives.
ACTIONS :
When administered alone, protamine has an anticoagulant effect. However, when it is given in the presence of heparin (which is strongly acidic), a stable salt is formed and the anticoagulant activity of both drugs is lost.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Protamine sulphate has a rapid onset of action. Neutralization of heparin occurs within 5 minutes after intravenous administration of an appropriate dose of protamine sulphate. Although the metabolic fate of the heparin-protamine complex has not been elucidated, it has been postulated that protamine sulphate in the heparin-protamine complex may be partially metabolized or may be attacked by fibrinolysin, thus freeing heparin.
INDICATIONS :
Protamine sulphate is indicated in the treatment of heparin overdosage.
Administration :
By slow intravenous injection only.
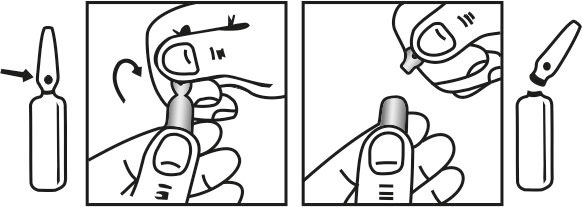
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Dosage :
Each mg of protamine sulphate neutralizes approximately 90 USP units of heparin activity derived from lung tissue or about 115 USP units of heparin activity derived from intestinal mucosa.
Protamine Sulphate Injection should be given by very slow intravenous injection over a 10-minute period in doses not to exceed 50 mg. Protamine sulphate is intended for injection without further dilution; however, if further dilution is desired, 5 % Dextrose in Water or Normal Saline may be used. Diluted solutions should not be stored since they contain no preservative. Protamine sulphate should not be mixed with other drugs without knowledge of their compatibility because protamine sulphate has been shown to be incompatible with certain antibiotics, including several of the cephalosporins and penicillins. Because heparin disappears rapidly from the circulation, the dose of protamine sulphate required also decreases rapidly with the time elapsed following intravenous injection of heparin. For example, if protamine sulphate is administered 30 minutes after heparin, one half the usual dose may be sufficient. The dosage of protamine sulphate should be guided by blood coagulation studies.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Protamine sulphate is contraindicated in patients who have shown previous intolerance to the drug.
WARNINGS :
Hyperheparinemia or bleeding has been reported in experimental animals and in some patients 30 minutes to 18 hours after cardiac surgery (under cardiopulmonary bypass) in spite of complete neutralization of heparin by adequate doses of protamine sulphate at the end of the operation. It is important to keep the patient under close observation after cardiac surgery. Additional doses of protamine sulphate should be administered if indicated by coagulation studies, such as the heparin titration test with protamine and the determination of plasma thrombin time.
Pregnancy Category C :
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with protamine sulphate. It is also not known whether protamine sulphate can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Protamine sulphate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers :
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when protamine sulphate is administered to a nursing woman.
Paediatric Use :
Safety and effectiveness in paediatric patients have not been established.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Protamine sulphate has been shown to be incompatible with certain antibiotics, including several of the cephalosporins and penicillins.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The intravenous administration of protamine sulphate may cause a sudden fall in blood pressure and bradycardia. Other reactions include transitory flushing and feeling of warmth, dyspnoea, nausea, vomiting, and lassitude. Back pain has been reported in conscious patients undergoing such procedures as cardiac catheterization. Severe adverse reactions have been reported including :
1. Anaphylaxis that resulted in severe respiratory distress, circulatory collapse and capillary leak. Fatal anaphylaxis has been reported in one patient with no prior history of allergies;
2. Anaphylactoid reactions with circulatory collapse, capillary leak, and noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema; acute pulmonary hypertension.
Complement activation by the heparin-protamine complexes, release of lysosomal enzymes from neutrophils, and prostaglandin and thromboxane generation have been associated with the development of anaphylactoid reactions. Severe and potentially irreversible circulatory collapse associated with myocardial failure and reduced cardiac output can also occur. The mechanism(s) of this reaction and the role played by concurrent factors are unclear. High-protein, noncardiogenic pulmonary oedema associated with the use of protamine has been reported in patients on cardiopulmonary bypass who are undergoing cardiovascular surgery. The etiologic role of protamine in the pathogenesis of this condition is uncertain, and multiple factors have been present in most cases. The condition has been reported in association with administration of certain blood products, other drugs, cardiopulmonary bypass alone, and other etiologic factors. It is difficult to treat, and it can be life threatening. Because fatal anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported after the administration of protamine sulphate, the drug should be given only when resuscitation techniques and treatment of anaphylactic and anaphylactoid shock are readily available.
OVERDOSAGES :
Signs and Symptoms :
Overdose of protamine sulphate may cause bleeding. Protamine has a weak anticoagulant effect due to an interaction with platelets and with many proteins including fibrinogen. This effect should be distinguished from the rebound anticoagulation that may occur 30 minutes to 18 hours following the reversal of heparin with protamine. Rapid administration of protamine is more likely to result in bradycardia, dyspnoea, a sensation of warmth, flushing and severe hypotension. Hypertension has also occurred.The median lethal intravenous dose of protamine sulphate is 50 mg/kg in mice. Serum concentrations of protamine sulphate are not clinically useful. Information is not available on the amount of drug in a single dose that is associated with overdosage or is likely to be life threatening.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGES :
In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs and unusual drug kinetics in your patient. Replace blood loss with blood transfusions or fresh frozen plasma. If the patient is hypotensive, consider fluids, epinephrine, dobutamine or dopamine.
PHARMACEUTICAL PRECAUTIONS :
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
STORAGE :
Store in a refrigerator between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
Do not freeze.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacturing.
PRESENTATION :
Protide is supplied as per below table :
| Strength | Pack Size | Packing |
| 10 mg/ml | 5 ml Ampoule | 5 Ampoules |
| 10 mg/ml | 5 ml Vial | 5 Vial |
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular