2.5 mg, 5 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
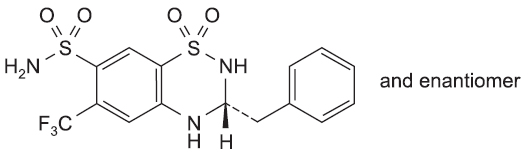
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. (Bendroflumethiazide) is a potent oral diuretic and antihypertensive agent. Chemically, Bendroflumethiazide is (3RS)-3-Benzyl-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide1,1-dioxide. The molecular formula is C15H14F3N3O4S2 and molecular weight is 421.4.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is white coloured, circular, biconvex tablet having breakline on one side and other side plain.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Bendroflumethiazide B.P. 2.5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Bendroflumethiazide B.P. 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Bendroflumethiazide is a thiazide diuretic.The mechanism whereby the thiazides exert their antihypertensive effect has not been clearly established. Bendroflumethiazide inhibits the renal tubular absorption of salt and water by its action at the beginning of the distal convoluted tubule. Sodium and chloride ions are excreted in equivalent proportions. Because potassium excretion is promoted, metabolic alkalosis may occur secondary to hypokalaemia. There is no important effect upon carbonic anhydrase. Bendroflumethiazide exerts its diuretic effect in about 2 hours and this lasts for 12 to 18 hours or longer.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption :
Bendroflumethiazide has been reported to be completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Diuresis is initiated in about 2 hours and lasts for 12-18 hours or longer.
Distribution :
Bendroflumethiazide is more than 90 % bound to plasma proteins.
Metabolism :
There are indications that it is fairly extensively metabolised. Peak plasma levels are reached in 2 hours and a plasma half- life of between 3 and 8.5 hours on average.
Elimination :
About 30 % is excreted unchanged in the urine with the remainder excreted as uncharacterized metabolites.
INDICATIONS :
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is indicated in the treatment of oedema associated with conditions such as : congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome and cirrhosis of the liver. BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is indicated in the treatment of essential hypertension where it may be used as the sole antihypertensive agent, or as an adjunct to other medicines whose action it potentiates. BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is used for suppress lactation. BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is also used in the management of idiopathic hypercalciuria.
Administration :
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is for oral administration.
Dosage :
Adults :
Hypertension :
2.5 mg in the morning. Higher doses are rarely necessary. The tablets may be used in conjunction with other anti-hypertensive agents.
Oedema :
5 - 10 mg daily in the morning initially and a maintenance dose of 2.5 – 10 mg up to three times a week.
Suppression of lactation :
5 mg to be taken morning and mid-day for about five days.
Idiopathic hypercalciuria :
The condition is managed by increasing fluid intake and giving bendroflumethiazide in a dose of 2.5 mg daily (a higher dose is not usually necessary).
Elderly :
The dosage may need to be reduced particularly when renal function is impaired because of the possibility of electrolyte imbalance.
Children :
Dosage can be up to 400 µg/kg body weight daily initially with a maintenance dose of 50 – 100 µg/kg daily.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is contraindicated in patients with :
- Hypersensitivity to thiazides and any other ingredient in this product or other sulfonamide-derived drugs.
- Severe renal or hepatic insufficiency.
- Hypercalcaemia; refractory hypokalaemia; hyponatraemia; symptomatic hyperuricaemia.
- Addison’s disease and concurrent lithium therapy.
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
When treatment with bendroflumethiazide is intensive or continuous, periodic estimations of serum electrolytes (especially potassium) should be carried out. Some loss of potassium may occur and, in these circumstances, potassium chloride supplements may be required in the following cases :
- if the patient is vomiting, has diarrhoea or is suffering from an acute febrile or chronic illness (especially cirrhosis of the liver or heart failure).
- to prevent hypokalaemia, possible arrhythmias and other ECG changes in patients receiving digitalis especially if diuretic treatment is prolonged.
- in patients at risk of myocardial infarction.
- in patients admitted for cardiac surgery.
- in patients receiving concurrent therapy with carbenoxolone or corticosteroids.
Potassium depletion may cause polyuria, malaise, muscle weakness or cramp, decreased tendon reflexes, anorexia, dizziness, nausea or vomiting. Also, sensitivity to digitalis may increase and signs of overdosage appear. Prolonged potassium deficiency may induce chronic pyelonephritis. Potassium supplements must not be given in renal insufficiency complicated by hypocalcaemia. In renal insufficiency, renal function should be monitored. In prolonged therapy it is necessary to test for glycosuria and investigate polyuria. The possibility of magnesium depletion should be considered. In cirrhosis of the liver, thiazides may precipitate hepatic encephalopathy. Thiazides may aggravate existing diabetes mellitus and cause symptoms in patients with latent disease. Bendrofluazide may impair control of diabetes in patients receiving sulphonylureas. Thiazides should be used with caution in systemic lupus erythematosus. Serum uric acid levels may be raised in some patients, with or without gout. Thiazides may cause or aggravate hyperlipidaemia.
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Category C
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. is best avoided for the management of oedema or hypertension in pregnancy as it crosses the placenta and its use may be associated with hypocalcaemia, increased blood viscosity and reduced placental perfusion. There is insufficient evidence of safety in human pregnancy and foetal bone marrow depression, thrombocytopenia and neonatal jaundice have been described.
Nursing mothers :
Bendroflumethiazide suppresses lactation and, although the amounts passing into breast milk are small, it should be avoided in breast feeding mothers.
Paediatric Use :
Safety and effectiveness in children have not ben established.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Allopurinol :
Bendroflumethiazide may antagonise the action of allopurinol by causing retention of urate in the kidney. Caution is advised when using this combination.
Anion exchange resins :
Colestyramine and colestipol reduce absorption of bendroflumethiazide. This can be prevented by leaving an interval of two hours between doses of bendroflumethiazide and the anion exchange resin.
Antiarrhythmics :
The cardiotoxicity of disopyramide, amiodarone, flecainide and quinidine is increased if hypokalaemia occurs following the administration of bendroflumethiazide. The actions of lidocaine and mexiletine are antagonised by hypokalaemia.
Antidepressants :
There is an increased risk of postural hypotension if bendroflumethiazide is given with tricyclic antidepressants. There may also be a risk of hypokalaemia if thiazides are given with reboxetine. Concomitant use with MAOIs may result in an enhanced hypotensive effect.
Antidiabetics :
Bendroflumethiazide antagonises the hypoglycaemic effects of sulfonylureas, with a potential loss of diabetic control.
Antiepileptics :
There is an increased risk of hyponatraemia when bendroflumethiazide and carbamazepine are take concurrently.
Antifungals :
The risk of hypokalaemia is increased when amphotericin and bendroflumethiazide are taken concurrently.
Antihypertensives :
Bendroflumethiazide may enhance the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists. There is an increased risk of first dose hypotension if prazosin is given to a patient taking bendroflumethiazide.
Antipsychotics :
Hypokalaemia increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias with pimozide or thioridazine so concomitant use should be avoided.
Calcium salts :
Bendroflumethiazide reduces urinary excretion of calcium so there is an increase risk of hypercalcaemia when calcium salts are taken concurrently. Serum calcium levels should be monitored to ensure that they do not become excessive.
Calcium channel blockers and peripheral vasodilators :
The hypotensive effect of calcium channel blockers and moxisylyte may be enhanced when co-administered with bendroflumethiazide.
Corticosteroids :
Corticosteroids may exacerbate hypokalaemia associated with bendroflumethiazide and its diuretic activity may be antagonised.
Cytotoxics :
Concomitant use with cisplatin can lead to an increased risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
Digoxin :
The hypokalaemic effect of bendroflumethiazide may enhance sensitivity to digoxin when taken concurrently. Patients should be monitored for signs of digoxin intoxication, especially arrhythmias. The dose of digoxin should be reduced and potassium supplements given, should digoxin toxicity develop.
Hormone antagonists :
There is an increased risk of hyponatraemia when bendroflumethiazide is used concomitantly with aminoglutethamide. Bendroflumethiazide can cause an increased risk of hypercalcaemia when co-administered with toremifene.
Lithium :
Bendroflumethiazide inhibits the tubular elimination of lithium, resulting in an elevated plasma lithium concentration and risk of toxicity. Plasma lithium concentrations must be monitored when these drugs are given concurrently.
Muscle relaxants :
The hypotensive activity of bendroflumethiazide may be increased by baclofen and tizanidine. Bendroflumethiazide may enhance the neuromuscular blocking activity of non-depolarising muscle relaxants, such as tubocurarine, gallamine, alcuronium and pancuronium.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) :
Bendroflumethiazide may enhance the nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs. Indometacin and ketorolac antagonise the diuretic effect of bendroflumethiazide, this occurs to a lesser extent with ibuprofen, piroxicam and naproxen. The effects of concurrent use should be monitored and the dose of bendroflumethiazide modified if necessary.
Oestrogens and progestogens :
Oestrogens and combined oral contraceptives antagonise the diuretic effect of bendroflumethiazide.
Sympathomimetics :
Sympathomimetics can cause hypokalaemia. The risk of serious heart arrhythmias in asthmatic patients may be increased if bendroflumethiazide is added to their medication.
Theophylline :
Concomitant administration of theophylline and bendroflumethiazide increases the risk of hypokalaemia.
Ulcer healing drugs :
There is an increased risk of hypokalaemia and a decrease in diuretic activity when carbenoxolone and bendroflumethiazide are taken together. Patients should be monitored and given potassium supplements when required.
Vitamins :
The risk of hypercalcaemia is increased if bendroflumethiazide is given with vitamin D.
Drug/Laboratory tests intereactions :
Bendroflumethiazide may produce false-negative results with the phentolamine and tyramine tests; may interfere with the phenosulfonphthalein test due to decreased excretion; and it may cause diagnostic interference of serum electrolyte levels, blood and urine glucose levels, and a decrease in serum PBI levels without signs of thyroid disturbance.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Effects on blood :
Rarely, blood dyscrasias, including agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, thrombocytopenia and leucopenia, have been reported.
Hypersensitivity reactions :
Rashes (including exfoliative dermatitis), photosensitivity, pneumonitis and pulmonary oedema have been reported occasionally.
Metabolic effects :
Bendroflumethiazide may lower carbohydrate tolerance and the insulin dosage of some diabetic patients may require adjustment. Care is required when bendroflumethiazide is administered to patients with a known predisposition to diabetes. Bendroflumethiazide may raise serum uric acid levels and exacerbate gout in susceptible individuals. Plasma lipids may be altered in patients taking bendroflumethiazide.
Effects on electrolytes :
Bendroflumethiazide administration may cause hypokalaemia, hypomangnesaemia, hyponatraemia, hypercalcaemia and hypochloraemic alkalosis. Hypokalaemia may result in polyuria, malaise, muscle weakness or cramp, dizziness, nausea, anorexia or vomiting.
Gastrointestinal effects :
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation and gastric irritation have all been reported.
Other reactions :
Pancreatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis and impotence (reversible on discontinuing the drug) have been reported. Postural hypotension or dizziness may also occur.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
As bendroflumethiazide can cause dizziness, patients should make sure they are not affected before driving or operating machinery.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
The patient should be advised to take the medication at the same time each day as prescribed to minimize the inconvenience of diuresis, warned against interruption or discontinuation of medication even though he may feel well, and advised about a proper course in the event of an inadvertent missed dose. The patients should be informed of symptoms that would suggest potential adverse effects and told to report them prompty.
OVERDOSAGE :
Symptoms :
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dehydration, dizziness, weakness, muscle cramps, diuresis, increased frequency of micturition with polyuria and thirst. Extreme cases may show depletion of intravascular volume, hypotension and peripheral circulatory failure. Hypokalaemia and mild hypoglycaemia are likely to be present if diuresis is profound. CNS depression (e.g. drowsiness, lethargy and coma) may occur without cardiovascular or respiratory depression.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Activated charcoal may help reduce absorption of substantial amounts if given within one hour of ingestion. Treatment should be symptomatic and directed at fluid and electrolyte replacement which should be monitored together with the blood pressure and renal function. Hyponatraemia should be treated with water deprivation rather than by the administration of sodium chloride. Cathartics should be avoided.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light. Do not refrigerate. Avoid excessive heat.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
BENDROFLUMETHIAZIDE TABLETS B.P. contains Bendroflumethiazide B.P. 2.5 mg / 5 mg.
10 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular