25 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
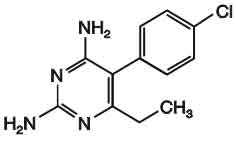
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. (Pyrimethamine) is dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor; antiprotozoal. Chemically, Pyrimethamine is 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethylpyrimidine-2, 4-diamine. The molecular formula is C12H13ClN4 and molecular weight is 248.7.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is white coloured, circular, biconvex tablets having score line on one side and “SGP” embossed on the other side of each tablet.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Pyrimethamine B.P. 25 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Pyrimethamine is an inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). It blocks the reduction of dihydrofolic acid to tetrahydrofolic acid which is an essential coenzyme in the production of nucleic acids, thereby leading to disruption of protein synthesis and nuclear division. The affinity of pyrimethamine for protozoal dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) is much greater than that for the mammalian enzyme. Sulphonamides act synergistically with pyrimethamine by arresting production of dihydrofolic acid from para-aminobenzoic acid. This results in sequential blockade of the folate pathway of Toxoplasma which, in contrast to man, is unable to utilize preformed folate.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption :
Pyrimethamine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after administration. Time to peak plasma concentration is 2 to 4 hours in healthy volunteers. Peak plasma concentrations vary widely between individuals and can range from 260 to 1411 ng/ml after daily doses of 25 mg. A similar degree of inter-patient variability in serum levels has been noted in patients with AIDS.
Distribution :
The volume of distribution for pyrimethamine is approximately 2 l/kg. In patients with HIV infection, population pharmacokinetic analysis has indicated that the mean volume of distribution is 246+/-64 l. About 87 % of the drug is bound to plasma proteins. Pyrimethamine has been shown to reach the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with AIDS given daily doses, achieving concentrations approximately one fifth of those in serum.
Metabolism and elimination :
Pyrimethamine is predominantly eliminated by metabolism, with up to 30 % recovered in the urine as parent compound over a period of several weeks. The mean elimination half-life is 85 hours (ranging from 35 to 175 hours). In AIDS patients, the total clearance is 1.28+/-0.41 l/hour resulting in an elimination half life of 139+/-34 hour. Data are lacking on the nature of the metabolites of pyrimethamine, their route/rate of formation and elimination in man and any pharmacological activity, particularly after prolonged daily dosing.
Multiple dose studies indicate that steady state is achieved in 12 to 20 days with daily dosing. It is theoretically possible that metabolic pathways might be saturable, leading to excessive accumulation of the drug in some patients. However, it has been demonstrated that plasma levels are approximately proportional to dose at steady state so this appears unlikely. Genetic variation in the exposure to pyrimethamine has been reported but these data are unsubstantiated.
INDICATIONS :
Treatment of Toxoplasmosis :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is indicated for the treatment of toxoplasmosis when used conjointly with a sulfonamide, since synergism exists with this combination.
Treatment of Acute Malaria :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is also indicated for the treatment of acute malaria. It should not be used alone to treat acute malaria. Fast-acting schizonticides such as chloroquine or quinine are indicated and preferable for the treatment of acute malaria. However, conjoint use of Pyrimethamine with a sulfonamide (e.g. sulfadoxine) will initiate transmission control and suppression of susceptible strains of plasmodia.
Chemoprophylaxis of Malaria :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is indicated for the chemoprophylaxis of malaria due to susceptible strains of plasmodia. However, resistance to pyrimethamine is prevalent worldwide. It is not suitable as a prophylactic agent for travelers to most areas.
Administration :
FOR ORAL USE.
The drug may be taken with meals to minimize anorexia and vomiting.
Dosage :
For Treatment of Toxoplasmosis :
The dosage of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. for the treatment of toxoplasmosis must be carefully adjusted so as to provide maximum therapeutic effect and a minimum of side effects. At the dosage required, there is a marked variation in the tolerance to the drug. Young patients may tolerate higher doses than older individuals. Concurrent administration of folinic acid is strongly recommended in all patients. The adult starting dose is 50 to 75 mg of the drug daily, together with 1 to 4 g daily of a sulfonamide of the sulfapyrimidine type, e.g. sulfadoxine. This dosage is ordinarily continued for 1 to 3 weeks, depending on the response of the patient and tolerance to therapy. The dosage may then be reduced to about one half that previously given for each drug and continued for an additional 4 to 5 weeks. The paediatric dosage of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is 1 mg/kg/day divided into 2 equal daily doses; after 2 to 4 days this dose may be reduced to one half and continued for approximately 1 month. The usual paediatric sulfonamide dosage is used in conjunction with PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P.
For Treatment of Acute Malaria :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is not recommended alone in the treatment of acute malaria. Fast-acting schizonticides, such as chloroquine or quinine, are indicated for treatment of acute malaria. However, PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. at a dosage of 25 mg daily for 2 days with a sulfonamide will initiate transmission control and suppression of non-falciparum malaria. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. is only recommended for patients infected in areas where susceptible plasmodia exist. Should circumstances arise wherein PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. must be used alone in semi-immune persons, the adult dosage for acute malaria is 50 mg for 2 days; children 4 through 10 years old may be given 25 mg daily for 2 days. In any event, clinical cure should be followed by the once-weekly regimen described below for chemoprophylaxis. Regimens which include suppression should be extended through any characteristic periods of early recrudescence and late relapse, i.e., for at least 10 weeks in each case.
For Chemoprophylaxis of Malaria :
Adults and paediatric patients over 10 years — 25 mg (1 tablet) once weekly
Children 4 through 10 years — 12.5 mg (1/2 tablet) once weekly
Infants and children under 4 years — 6.25 mg (1/4 tablet) once weekly
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should not be given to patients with a history of pyrimethamine sensitivity. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should not be used during the first trimester of pregnancy, megaloblastic anaemia secondary to folate deficiency. Breast-feeding should be avoided during toxoplasmosis treatment. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
The dosage of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. required for the treatment of toxoplasmosis is 10 to 20 times the recommended antimalaria dosage and approaches the toxic level. If signs of folate deficiency develop reduce the dosage or discontinue the drug according to the response of the patient. Folinic acid should be administered in a dosage of 5 to 15 mg daily (orally, IV, or IM) until normal haematopoiesis is restored. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. has been reported to produce a significant increase in the number of lung tumors in mice when given intraperitoneally at doses of 25 mg/kg. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should be kept out of the reach of infants and children as they are extremely susceptible to adverse effects from an overdose. Deaths in paediatric patients have been reported after accidental ingestion.
PRECAUTIONS :
The recommended dosage of chemoprophylaxis of malaria should not be exceeded. A small “starting” dose for toxoplasmosis is advised in patients with convulsive disorders to avoid the potential nervous system toxicity of pyrimethamine. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should be administered with caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function or in patients with possible folate deficiency, such as individuals with malabsorption syndrome, alcoholism, or pregnancy. Semiweekly blood and platelet counts are recommended for patients being treated for toxoplasmosis. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Teratogenic Effects : Category C
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. has been shown to be teratogenic in rats when given in oral doses 7 times the human dose for chemoprophylaxis of malaria or 2.5 times the human dose for treatment of toxoplasmosis. At these doses in rats, there was a significant increase in abnormalities such as cleft palate, brachygnathia, oligodactyly, and microphthalmia. Pyrimethamine has also been shown to produce terata such as meningocele in hamsters and cleft palate in miniature pigs when given in oral doses 170 and 5 times the human dose, respectively, for chemoprophylaxis of malaria or for treatment of toxoplasmosis. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus. Concurrent administration of folinic acid is strongly recommended when used for the treatment of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy.
Nursing mothers :
Pyrimethamine is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from pyrimethamine and from concurrent use of a sulfonamide with PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. for treatment of some patients with toxoplasmosis, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Use :
There is insufficient data to provide specific dose recommendations in children under 5 year. This formulation is not suitable for children under 5 years.
Geriatric Use :
Clinical studies of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Pyrimethamine may be used with sulfonamides, quinine and other antimalarials, and with other antibiotics. However, the concomitant use of other antifolic drugs or agents associated with myelosuppression including sulfonamides or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combinations, proguanil, zidovudine, or cytostatic agents (e.g., methotrexate), while the patient is receiving pyrimethamine, may increase the risk of bone marrow suppression. If signs of folate deficiency develop, pyrimethamine should be discontinued. Folinic acid should be administered until normal haematopoiesis is restored. Mild hepatotoxicity has been reported in some patients when lorazepam and pyrimethamine were administered concomitantly.
SIDE EFECTS :
Hypersensitivity reactions, occasionally severe (such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, and anaphylaxis), and hyperphenylalaninaemia, can occur particularly when pyrimethamine is administered concomitantly with a sulfonamide. Consult the complete prescribing information for the relevant sulfonamide for sulfonamide-associated adverse events. With doses of pyrimethamine used for the treatment of toxoplasmosis, anorexia and vomiting may occur. Vomiting may be minimized by giving the medication with meals; it usually disappears promptly upon reduction of dosage. Doses used in toxoplasmosis may produce megaloblastic anaemia, leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia, pancytopaenia, atrophic glossitis, hematuria, and disorders of cardiac rhythm. Haematologic effects, however, may also occur at low doses in certain individuals. Pulmonary eosinophilia has been reported rarely.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Patients should be warned that at the first appearance of a skin rash they should stop use of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. and seek medical attention immediately. Patients should also be warned that the appearance of sore throat, pallor, purpura, or glossitis may be early indications of serious disorders which require treatment with PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. to be stopped and medical treatment to be sought. Women of childbearing potential who are taking PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. should be warned against becoming pregnant. Concurrent administration of folinic acid is strongly recommended when used for the treatment of toxoplasmosis in all patients.
OVERDOSAGE :
Symptoms and signs :
Vomiting and convulsions occur in cases of severe, acute overdoses. Ataxia, tremor and respiratory depression can also occur. There have been isolated cases with fatal outcomes following acute overdose of PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. Chronic excess doses can result in bone marrow depression (e.g. megaloblastic anaemia, leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia) resulting from folic acid deficiency.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Routine supportive treatment, including maintenance of a clear airway and control of convulsions. Adequate fluids should be given to ensure optimal diuresis. To counteract possible folate deficiency, calcium folinate should be given until signs of toxicity have subsided. There may a delay of 7 to 10 days before the full leucopaenic side effects become evident; therefore calcium folinate therapy should be continued for the period at risk.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light. Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
PYRIMETHAMINE TABLETS B.P. contains Pyrimethamine B.P. 25 mg
10 blisters of 10 tablets per box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular