400 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
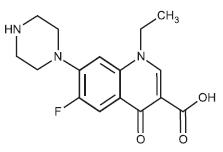
NOrFLOXACIN TABLETS USP (Norfloxacin) is a synthetic, broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Chemically, Norfloxacin is 1-Ethyl-6-fluoro-1, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. The molecular formula is C16H18FN3O3 and molecular weight is 319.33.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP are white coloured, elongated, biconvex, film coated tablets having breakline on one side and plain on other side.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Norfloxacin USP 400 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide USP
ACTIONS :
Norfloxacin is bactericidal and acts by inhibiting bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis. Norfloxacin is a broad-spectrum anti-infective, active against a wide range of aerobic gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. The fluorine atom at the 6 position
increases potency against gram-negative organisms, and the piperazine moiety at the 7 position is responsible for anti-pseudomonal activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
About 30 to 40 % of an oral dose of norfloxacin is absorbed. Peak plasma concentrations of about 1.5 micrograms/ml have been achieved 1 to 2 hours after a 400-mg oral dose; the presence of food can delay absorption. The plasma half-life is 3 to 4 hours and may be prolonged in renal impairment; a value of 6.5 hours or more has been reported when creatinine clearance is below 30 ml/minute. Norfloxacin has been reported to be 14 % bound to plasma proteins. It is probably widely distributed, but information is limited. Norfloxacin penetrates well into tissues of the genito-urinary tract. It crosses the placenta. Relatively high concentrations are achieved in bile. About 30 % of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours, producing high urinary concentrations : norfloxacin is least soluble at a urinary pH of 7.5. Urinary excretion is by tubular secretion and glomerular filtration and is reduced by probenecid, although plasma concentrations of norfloxacin are not generally affected. Some metabolism occurs, possibly in the liver, and several metabolites have been identified in urine, some with antibacterial activity. About 30 % of an oral dose is recovered from the faeces.
MICROBIOLOGY :
Norfloxacin has in vitro activity against a broad range of gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic bacteria. The fluorine atom at the 6 position provides increased potency against gram-negative organisms, and the piperazine moiety at the 7 position is responsible for anti-pseudomonal activity. Norfloxacin inhibits bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and
is bactericidal. At the molecular level, three specific events are attributed to norfloxacin in E. coli cells :
1. inhibition of the ATP-dependent DNA supercoiling reaction catalyzed
2. DNA gyrase.
3. inhibition of the relaxation of supercoiled DNA.
4. promotion of double-stranded DNA breakage.
Resistance to norfloxacin due to spontaneous mutation in vitro is a rare occurrence (range : 10-9 to 10-12 cells). Resistant organisms have emerged during therapy with norfloxacin in less than 1 % of patients treated. Organisms in which development of resistance is greatest
are the following :
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Acinetobacter spp.
Enterococcus spp.
ethicillin - resistant Staphylococcus aureus
For this reason, when there is a lack of satisfactory clinical response, repeat culture and susceptibility testing should be done. Nalidixic acid-resistant organisms are generally susceptible to norfloxacin in vitro; however, these organisms may have higher minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) to norfloxacin than nalidixic acid-susceptible strains. There is generally no cross-resistance between norfloxacin and other classes of antibacterial agents. Therefore, norfloxacin may demonstrate activity against indicated organisms resistant to some other antimicrobial agents including the aminoglycosides, penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides, and sulfonamides, including combinations of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Antagonism has been demonstrated in vitro between norfloxacin and nitrofurantoin. Norfloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections :
Gram-positive aerobes :
Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus agalactiae
Gram-negative aerobes :
Citrobacter freundii
Enterobacter aerogenes
Enterobacter cloacae
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Serratia marcescens. The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown Norfloxacin exhibits in vitro minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC’s) of </=4 μg/ml against most (>/=90 %) strains of the following
microorganisms; however, the safety and effectiveness of norfloxacin in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-negative aerobes :
Citrobacter diversus
Edwardsiella tarda
Enterobacter agglomerans
Haemophilus ducreyi
Klebsiella oxytoca
Morganella morganii
Providencia alcalifaciens
Providencia rettgeri
Providencia stuartii
Pseudomonas fluorescens
Pseudomonas stutzeri
Other :
Ureaplasma urealyticum
Norfloxacin is not generally active against obligate anaerobes. Norfloxacin has not been shown to be active against Treponema pallidum.
Susceptibility Tests :
Dilution Techniques :
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC’s). These MIC’s provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MIC’s should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method1 (broth, agar, or microdilution) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of norfloxacin powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria* :
| MIC (MG/ML) | Interpretation |
| </=4 | Susceptible (S) |
| 8 | INTERMEDIATE (S) |
| >/=16 | Resistance (R) |
A report of “Susceptible” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable. A report of “Intermediate” indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of “Resistant”
Administration :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP is for oral administration. NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should be taken with a glass of water at least one hour before or two hours after a meal or milk ingestion. Patients receiving norfloxacin should drink fluids liberally to be well hydrated. Multivitamins, products containing iron or zinc, antacids containing magnesium and aluminium, sucralfate, or didanosine (tablets and solution) should not be taken concomitantly or within 2 hours after dosing norfloxacin.
Dosage :
Susceptibility of the causative organism to norfloxacin should be tested prior to and during treatment if clinical response warrants. However, therapy may be initiated before obtaining the results of these tests. Maximum total daily dosage should not exceed 800 mg/day.
| Diagnosis | Dosage | Therapy Duration |
| Urinary tract infections | 400 mg twice daily | 7-10 days |
| Chronic relapsing urinary tract infection | 400 mg twice daily | Upto 12 days |
| Uncomplicated acute cystitis | 400 mg twice daily | 3 days |
| Chronic prostatitis | 400 mg twice daily | 4 days |
| Acute bacterial gastroenteritis | 400 mg twice daily | 5 days |
| Acute gonococcal urethritis, pharyngitis | 800 mg | Single Dose |
If adequate suppression is obtained within the first four weeks of therapy, the dose of norfloxacin may be reduced to 400 mg daily.
Renal impairment :
Doses of norfloxacin may need to be reduced in renal impairment; for urinary-tract infections, 400 mg once daily may be given to patients with a creatinine clearance of 30 ml/minute or less.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should not be used in :
- patients with known hypersensitivity to norfloxacin, any chemically related quinoline antibacterials or any component of this product.
- patients with a history of fluoroquinolone associated tendonopathy.
- pre-pubertal children.
- pregnant women.
Crystalluria :
Needle-shaped crystals were found in the urine of some volunteers who received either placebo, norfloxacin 800 mg or norfloxacin 1,600 mg (at or twice the recommended daily dose, respectively) while participating in a double blind, crossover study comparing single doses of norfloxacin with placebo. While crystalluria is not expected to occur under usual conditions with a dosage regimen of 400 mg twice daily, as a precaution, the daily recommended dosage should not be exceeded. Patient should drink sufficient fluids to ensure a proper state of hydration and adequate urinary output, and to avoid excessively alkaline urine with the use of urinary alkaliniser (e.g. Ural).
Pseudomembranous colitis :
Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with many antibiotics including norfloxacin. A toxin produced with Clostridium difficile appears to be the primary cause. The severity of the colitis may range from mild to life-threatening. It is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who develop diarrhoea or colitis in association with antibiotic use (this may occur up to several weeks after cessation of antibiotic therapy). Mild cases usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. However, in moderate to severe cases, appropriate therapy with a suitable oral antibacterial agent effective against C. difficile should be considered. Fluids, electrolytes and protein replacement should be provided when indicated. Drugs which delay peristalsis, e.g. opiates and diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil), may prolong and/or worsen the condition and should not be used.
Tendonitis and tendon rupture :
Fluoroquinolones, including norfloxacin, may cause tendonitis, achilles and other tendon ruptures. The risk of these adverse effects is present during use and for 6 months following use of fluoroquinolone. Also, the risk is increased in patients over the age of 60 years, on concomitant systemic steroid therapy, or who have a kidney, heart or lung transplant. Fluoroquinolones should not be used in patients with a history of fluoroquinolone associated tendonopathy. Prescribers should advise patients that at the first sign of tendon pain, inflammation or tendon rupture, to stop taking the fluoroquinolone, avoid exercise or use of the affected area, and immediately contact their doctors.
Seizures :
As with other organic acids, NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should be used with caution in individuals with a history of convulsions or known factors that predispose to seizures. Convulsions have been reported rarely in patients receiving norfloxacin.
Photosensitivity :
Photosensitivity reactions have been observed in patients who are exposed to excessive sunlight while receiving fluoroquinolones.Excessive sunlight should be avoided. Therapy should be discontinued if photosensitivity occurs.
Haemolytic reactions :
Rarely, haemolytic reactions have been reported in patients with latent or actual defects in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity who take quinolone agents, including norfloxacin.
Myasthenia gravis :
Quinolones, including norfloxacin, may exacerbate the signs of myasthenia gravis and lead to life-threatening weakness of the respiratory muscles. Caution should be exercised when using quinolones, including norfloxacin, in patients with myasthenia gravis.
Peripheral Neuropathy :
Cases of sensory or sensorimotor polyneuropathy resulting in paraesthesias, hypoaesthesias, dysaesthesias, or weakness have been reported in patients receiving fluoroquinolones including norfloxacin. Symptoms may occur soon after initiation of norfloxacin and may be irreversible. Patients under treatment with NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should be advised to inform their doctor if symptoms of neuropathy such as pain, burning, tingling, numbness or weakness or other alterations in sensations including light touch, pain, temperature, position sense and vibratory sensation develop. NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should be discontinued immediately if the patient experiences symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and the patient should be changed to a non-fluoroquinolone antibiotic.
Arrhythmia :
Some quinolones have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram and infrequent cases of arrhythmia. During post-marketing surveillance, extremely rare cases of torsades de pointes, have been reported in patients taking norfloxacin. These reports generally involve patients who had other concurrent medical conditions and the relationship to norfloxacin has not been established. Among drugs known to cause prolongation of the QT interval, the risk of arrhythmia may be reduced by avoiding use in the presence of hypokalaemia, significant bradycardia, or concurrent treatment with class IA or class III antiarrhythmic agents. Quinolones should also be used with caution in patients using cisapride, erythromycin, antipsychotics, tricyclic antidepressants or have any personal or family history of QTc prolongation.
Renal impairment :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP is suitable for the treatment of patients with renal impairment. However, since norfloxacin is primarily excreted by the kidney, urinary levels may be significantly compromised by severe renal dysfunction.
Laboratory tests :
As with any potent antibacterial agent, periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
Pregnancy : Category C
Adequate and well controlled studies in humans have not been done. Systemic norfloxacin crosses the placenta. The umbilical cord serum concentration ranged from undetectable to 0.5 mg/ml and the amniotic fluid concentration ranged from undetectable to 0.92 mg/ml
following the administration of a single 200 mg dose of norfloxacin. At oral doses 6 to 50 times the human oral dose, there has been no evidence of a teratogenic effect in rats, rabbits, mice, or monkeys. However, in monkeys administered oral doses 10 times the
maximum human oral dose (800 mg daily), norfloxacin has been shown to produce embryonic loss. Peak plasma levels reached 2 to 3 times those obtained in humans.
Nursing Mothers :
It is not known whether norfloxacin is distributed into breast milk. Systemic norfloxacin has not been detected in breast milk when it was given in low (200-mg) doses to nursing mothers. However, other systemic quinolone derivatives are distributed into breast milk, and
systemic norfloxacin causes arthropathy in immature animals. Therefore, use of norfloxacin is not recommended in nursing mothers.
Paediatric Use :
Appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of norfloxacin have not been performed in infants up to 1 year of age. Safety and efficacy have not been established. Although there is no information on norfloxacin, other quinolones have not been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals. In addition, there is no evidence that these quinolones have any effects on the weight-bearing joints.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP may alter a patient´s reactivity so that the ability to drive, operate machinery or work without firm support is impaired, especially at the start of treatment, on increasing the dosage or when switching medication and in conjunction with alcohol.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Quinolones, including norfloxacin, have been shown in vitro to inhibit CYP1A2. Concomitant use with drugs metabolised by CYP1A2 (e.g. caffeine, clozapine, ropinirole, tacrine, theophylline, tizanidine) may result in increased substrate drug concentrations when given in usual doses. Patients taking any of these drugs concomitantly with norfloxacin should be carefully monitored. Elevated plasma levels of theophylline have been reported with concomitant quinolone use. There have been reports of theophylline related side effects in patients on concomitant therapy with norfloxacin and theophylline. Therefore, monitoring of theophylline plasma levels should be considered and dosage of theophylline adjusted as required. Elevated serum levels of cyclosporine have been reported with concomitant use of cyclosporine with norfloxacin. Therefore cyclosporine serum levels should be monitored and appropriate cyclosporine dosage adjustments made when these drugs are used concomitantly.
Quinolones, including norfloxacin, may enhance the effects of the oral anticoagulant warfarin or its derivatives. When these products are administered concomitantly, prothrombin time or other suitable coagulation tests should be closely monitored. The concomitant administration of quinolones including norfloxacin with glibenclamide (a sulfonylurea agent) has, on rare occasions, resulted in severe hypoglycaemia. Monitoring of blood glucose is recommended when these agents are co-administered. Diminished urinary excretion of norfloxacin has been reported during the concomitant administration of probenecid and norfloxacin. The concomitant use of nitrofurantoin is not recommended since nitrofurantoin may antagonize the antibacterial effect of norfloxacin in the urinary tract. Multivitamins, or other products containing iron or zinc, antacids or sucralfate should not be administered concomitantly with, or within 2 hours of, the administration of norfloxacin, because they may interfere with absorption resulting in lower serum and urine levels of norfloxacin.
Didanosine chewable/buffered tablets or the paediatric powder for oral solution should not be administered concomitantly with, or within 2 hours of, the administration of norfloxacin, because these products may interfere with absorption resulting in lower serum and urine levels of norfloxacin. Some quinolones have also been shown to interfere with the metabolism of caffeine. This may lead to reduced clearance of caffeine and a prolongation of its plasma half-life. Concomitant administration of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with a quinolone, including norfloxacin, may increase the risk of stimulation of central nervous system and convulsive seizures. NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP should be used with caution in individuals receiving NSAIDs concomitantly. Animal data have shown that quinolones in combination with fenbufen can lead to convulsions. Concomitant administration of quinolones and fenbufen should be avoided.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The overall incidence of drug-related side effects reported during clinical trials was approximately 3 %. The most common side effects have been gastro-intestinal, neuropsychiatric and skin reactions, and include nausea, headache, dizziness, rash, heartburn, abdominal pain/cramps, and diarrhoea. Less commonly, other side effects such as anorexia, sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety/nervousness, irritability, euphoria, disorientation, hallucination, tinnitus, and epiphora have been reported. Abnormal laboratory side effects observed during clinical trials included : leucopenia, elevation of ALAT (SGPT), ASAT (SGOT), eosinophilia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia. With more widespread use the following additional side effects have been reported :
Hypersensitivity reactions :
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, dyspnoea, vasculitis, urticaria, arthritis, myalgia, arthralgia and interstitial nephritis.
Skin :
Photosensitivity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, pruritus, leukocytoclastic vasculitis.
Gastro-intestinal :
Pseudomembranous colitis, pancreatitis (rare), hepatitis, jaundice including cholestatic jaundice and elevated liver-function tests.
Musculoskeletal :
Tendinitis, tendon rupture, exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, elevated creatinine kinase (CK).
Nervous system/psychiatric :
Polyneuropathy including Guillaine-Barré syndrome, confusion, paraesthesia, hypoaesthesia, psychic disturbances including psychotic reactions, convulsions, tremors, myoclonus.
Haematological :
Agranulocytosis, haemolytic anaemia, sometimes associated with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Genito-urinary :
Vaginal candidiasis.
Renal function :
Renal failure.
Special senses :
Dysgeusia, visual disturbances, hearing loss.
Cardiovascular :
Frequency not known: ventricular arrhythmia and torsades de pointes (reported predominantly in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation), ECG QT prolonged.
OVERDOSAGE :
No significant lethality was observed in male and female mice and rats at single oral doses up to 4 g/kg.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment should be implemented. ECG monitoring should be undertaken, because of the possibility of QT interval prolongation. In the event of acute overdosage, the stomach should be emptied by induced vomiting or by gastric lavage. The patient should be carefully observed and given symptomatic and supportive treatment as required. Adequate hydration must be maintained to prevent crystalluria.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
NORFLOXACIN TABLETS USP contains Norfloxacin USP 400 mg.
3 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular