1 mg/0.5 ml, 10 mg/ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
PhytoKon (Pytomenadione - Vitamin K1) is a vitamin occurring naturally in plants (as phylloquinone) as well as produced synthetically. Chemically, phytomenadione is 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone. The molecular formula is C31H46O2 and molecular weight is 450.7.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
-Structure.jpg)
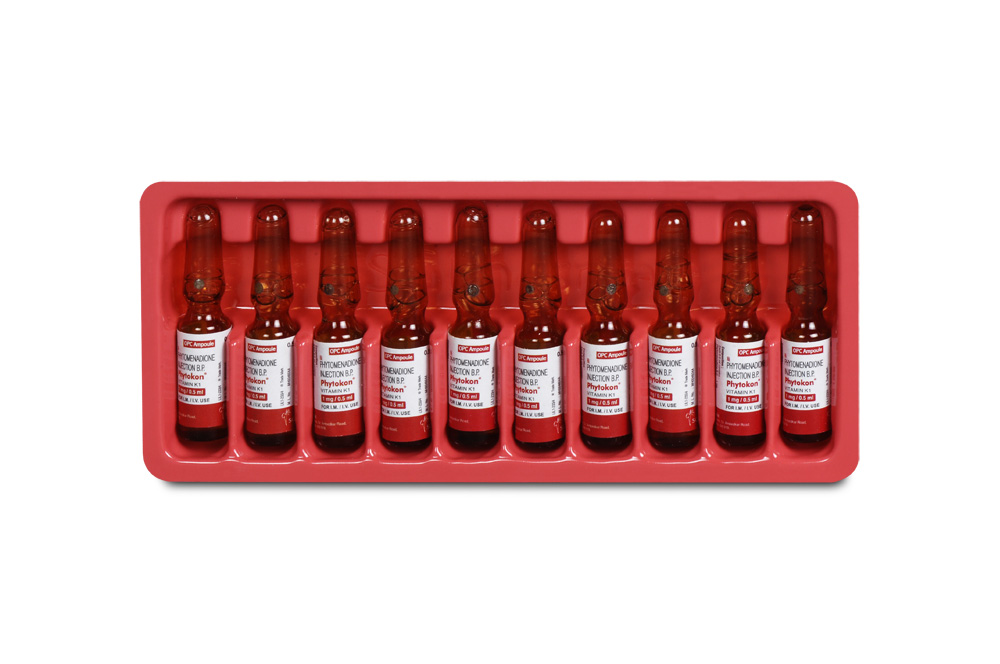
PHYTOKON is a sterile, yellow aqueous solution filled in amber glass ampoule of suitable size.
COMPOSITION :
Each 0.5 ml contains :
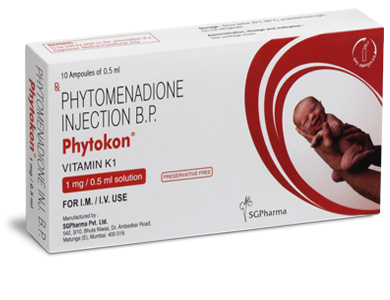
Phytomenadione B.P. 1 mg
Water for Injections I.P. q.s.
Contains no preservatives.
Each ml contains :
Phytomenadione B.P. 10 mg
Water for Injections I.P. q.s.
Contains no preservatives.
ACTIONS :
PHYTOKON aqueous solution of vitamin K1 for parenteral injection, possesses the same type and degree of activity as does naturally-occurring vitamin K, which is necessary for the production via the liver of active prothrombin (factor II), proconvertin (factor VII), plasma thromboplastin component (factor IX), and Stuart factor (factor X). The prothrombin test is sensitive to the levels of three of these four factors - II, VII, IX and X. Vitamin K is an essential cofactor for a microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the post-translational carboxylation of multiple, specific, peptide-bound glutamic acid residues in inactive hepatic precursors of factors II, VII, IX, and X. The resulting gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues convert the precursors into active coagulation factors that are subsequently secreted by liver cells into the blood. Phytomenadione is readily absorbed following intramuscular administration. After absorption, phytomenadione is initially concentrated in the liver, but the concentration declines rapidly. Very little vitamin K accumulates in tissues. Little is known about the metabolic fate of vitamin K. Almost no free unmetabolized vitamin K appears in bile or urine.
In normal animals and humans, phytomenadione is virtually devoid of pharmacodynamic activity. However, in animals and humans deficient in vitamin K, the pharmacological action of vitamin K is related to its normal physiological function, that is, to promote the hepatic biosynthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting factors. The action of the aqueous colloidal solution, when administered intravenously, is generally detectable within an hour or two and haemorrhage is usually controlled within 3 to 6 hours. A normal prothrombin level may often be obtained in 12 to 14 hours. In the prophylaxis and treatment of haemorrhagic disease of the newborn, phytomenadione has demonstrated a greater margin of safety than that of the water-soluble vitamin K analogues.
INDICATIONS :
PHYTOKON is indicated in the following coagulation disorders which are due to faulty formation of factors II, VII, IX, and X when caused by vitamin K deficiency or interference with vitamin K activity.
PHYTOKON injection is indicated in :
• anticoagulant-induced prothrombin deficiency caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives;
• prophylaxis and therapy of haemorrhagic disease of the newborn;
• hypoprothrombinemia due to antibacterial therapy;
• hypoprothrombinemia secondary to factors limiting absorption or synthesis of vitamin K, e.g., obstructive jaundice, biliary fistula, sprue, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, intestinal resection, cystic fibrosis of the pancreas, and regional enteritis;
• other drug-induced hypoprothrombinemia where it is definitely shown that the result is due to interference with vitamin K metabolism, e.g., salicylates.
Administration :
Whenever possible, PHYTOKON should be given by the subcutaneous or intramuscular route. When intravenous administration is considered unavoidable, the drug should be injected very slowly, not exceeding 1 mg per minute.
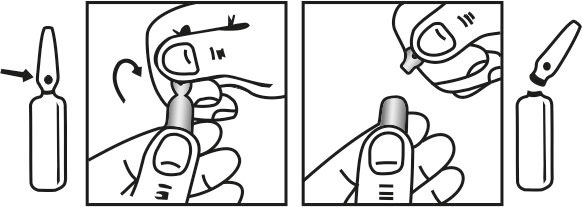
INSTRUCTION FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
DIRECTIONS FOR DILUTION :
PHYTOKON may be diluted with 0.9 % Sodium Chloride Injection, 5 % Dextrose Injection, or 5 % Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection. Benzyl alcohol as a preservative has been associated with toxicity in newborns. Therefore, all of the above diluents should be preservative-free. Other diluents should not be used. When dilutions are indicated, administration should be started immediately after mixture with the diluent, and unused portions of the dilution should be discarded, as well as unused contents of the ampoule.
Dosage :
Prophylaxis of Haemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn :
The American Academy of Paediatrics recommends that vitamin K1 be given to the newborn. A single intramuscular dose of PHYTOKON 0.5 to 1 mg within one hour of birth is recommended.
Treatment of Haemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn :
Empiric administration of vitamin K1 should not replace proper laboratory evaluation of the coagulation mechanism. A prompt response (shortening of the prothrombin time in 2 to 4 hours) following administration of vitamin K1 is usually diagnostic of haemorrhagic disease of the newborn, and failure to respond indicates another diagnosis or coagulation disorder. PHYTOKON 1 mg should be given either subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Higher doses may be necessary if the mother has been receiving oral anticoagulants.
Whole blood or component therapy may be indicated if bleeding is excessive. This therapy, however does not correct the underlying disorder and PHYTOKON should be given concurrently.
Anticoagulant-Induced Prothrombin Deficiency in Adults :
To correct excessively prolonged prothrombin time caused by oral anticoagulant therapy- 2.5 to 10 mg or up to 25 mg initially is recommended. In rare instances 50 mg may be required. Frequency and amount of subsequent doses should be determined by prothrombin time response or clinical condition. If in 6 to 8 hours after parenteral administration the prothrombin time has not been shortened satisfactorily, the dose should be repeated.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes in Adults :
A dosage of 2.5 to 25 mg or more (rarely up to 50 mg) is recommended, the amount and route of administration depending upon the severity of the condition and response obtained. If possible, discontinuation or reduction of the dosage of drugs interfering with coagulation mechanisms (such as salicylates, antibiotics) is suggested as an alternative to administering concurrent PHYTOKON. The severity of the coagulation disorder should determine whether the immediate administration of PHYTOKON is required in addition to discontinuation or reduction of interfering drugs.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Pregnancy : Pregnancy Category C :
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with PHYTOKON. It is also not known whether PHYTOKON can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. PHYTOKON should be given to pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when PHYTOKON is administered to a nursing woman.
Paediatric Use :
Haemolysis, jaundice, and hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, particularly in premature infants, may be related to the dose of PHYTOKON. Therefore, the recommended dose should not be exceeded.
Laboratory Tests :
rothrombin time should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of fertility :
Studies of carcinogenicity, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility have not been conducted with PHYTOKON.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Temporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants may result, especially when larger doses of phytomenadione are used. If relatively large doses have been employed, it may be necessary when reinstituting anticoagulant therapy to use somewhat larger doses of the prothrombin-depressing anticoagulant, or to use one which acts on a different principle, such as heparin sodium. Phytomenadione injection is physically incompatible with phenytoin injection.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactoid reactions and deaths have been reported following parenteral administration. The majority of these reported events occurred following intravenous administration. The possibility of allergic sensitivity, including an anaphylactoid reaction, should be kept in mind following parenteral administration. Transient "flushing sensations" and "peculiar" sensations of taste have been observed, as well as rare instances of dizziness, rapid and weak pulse, profuse sweating, brief hypotension, dyspnea, and cyanosis. Pain, swelling, and tenderness at the injection site may occur. Infrequently, usually after repeated injection, erythematous, indurated, pruritic plaques have occurred, rarely, these have progressed to scleroderma-like lesions that have persisted for long periods. In other cases, these lesions have resembled erythema perstans. Hyperbilirubinemia has been observed in the newborn following administration of phytomenadione. This has occurred rarely and primarily with doses above those recommended.
OVERDOSAGE :
The intravenous LD50 of PHYTOKON in the mouse is 41.5 and 52 ml/kg for the 0.2 % and 1 % concentrations, respectively.
PHARMACEUTICAL PRECAUTIONS :
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Vitamin K1 is fairly rapidly degraded by light; therefore, always protect PHYTOKON from light. Store PHYTOKON in closed original carton until contents have been used.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
PHYTOKON is supplied as 1 mg phytomenadione in 0.5 ml aqueous solution. Such 10 ampoules of 0.5 ml are packed in a Box.
PHYTOKON is supplied as 10 mg phytomenadione in 1 ml aqueous solution.
Such 10 ampoules of 1 ml are packed in a Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular