200,000 IU/ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
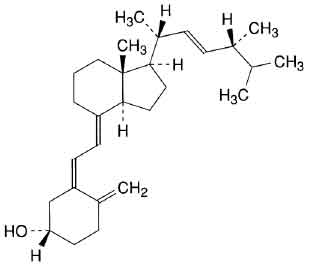
ERGOCALCIFEROL INJECTION (Ergocalciferol) is derived from fungal and plant sources. Ergocalciferol is also known as Vitamin D2. Its chemical names are 9, 10-seco (5Z, 7E)-5, 7, 10(19), 22-ergostatetraene-3beta-ol and (3 beta, 5Z, 7E, 22E)-9, 10-secoergosta-5, 7, 10(19), 22-tetraen-3-ol. Its molecular formula is C28H44O and its molecular weight is 396.66 daltons.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
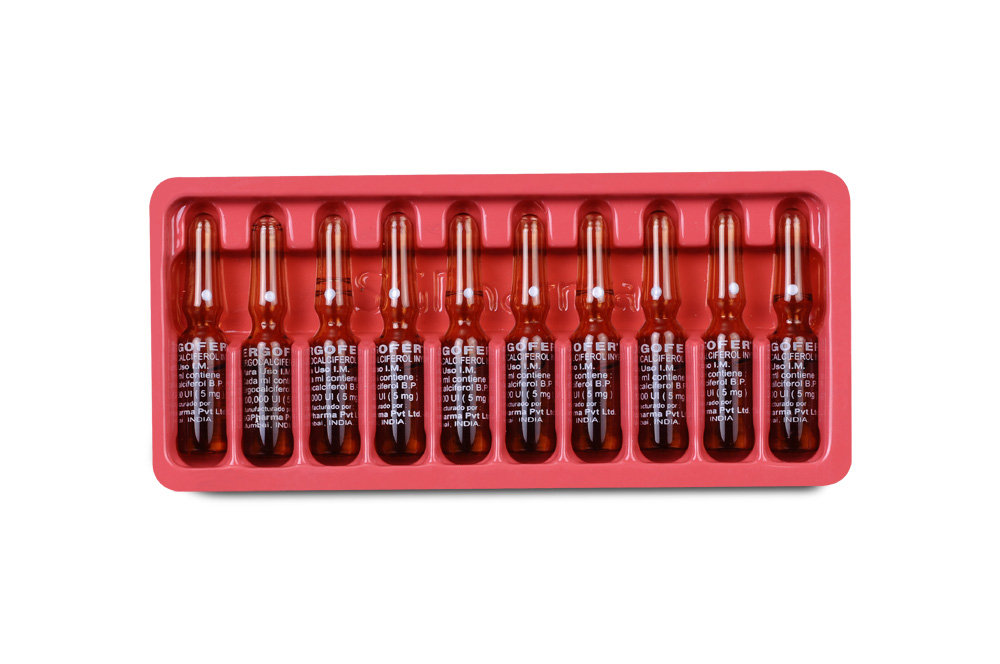
A pale yellow, oily liquid filled in 1 ml amber ampoule.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Ergocalciferol B.P. 2,00,000 IU (5 mg)
Ethyl Oleate B.P. q.s.
ACTIONS :
Ergocalciferol has the highest activity from the group of Vitamin D. It regulates : phosphorus-calcium metabolism and the processes of ossification; absorption of phosphorus and amino acids in renal tubules.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Vitamin D is absorbed in the jejunum wall and as calciferol crosses into the blood plasma and lymph. Its absorption depends on the functional condition of the pancreas and is strongly reduced in the presence of steatorrhea. Vitamin D2 and its metabolites circulates in the blood bound to a specific alpha-globulin. Vitamin D can be stored in adipose and muscle tissue for long period of time. It is slowly released from such storage sites and from the skin where it is formed in the presence of sunlight or ultraviolet light. Ergocalciferol have a slow onset and a long duration of action. The half-elimination time of Vitamin D is 26 hours. Ergocalciferol is hydroxylated in the liver by the enzyme Vitamin D 25-hydroxylase to form 25-hydroxyergocalciferol which undergo further hydroxylation in the kidneys by the enzyme Vitamin D1-hydroxylase to form the active metabolite 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol. Further metabolism also occurs in the kidneys, including the formation of the 1, 24, 25-trihydroxy derivatives. The half-elimination time of this active form is between 7 and 14 days.
Vitamin D and their metabolites are excreted mainly into the bile and faeces with only small amounts appearing in urine. They also undergo extensive enterohepatic recirculation.
INDICATIONS :
ERGOCALCIFEROL INJECTION is used prophylactically and for the treatment of refractory rickets (Vitamin D-resistant rickets), spasmophilia and osteomalacia, for acceleration of the coalescence of fractured bones, protection from dental caries, in osteoporosis, familial hypophosphataemia, hypocalcaemia associated with hypoparathyroidism, scrofula, exudative diathesis. ERGOCALCIFEROL INJECTION is also administered for the treatment of lupus, pleurisy and tuberculosis of the larynx, kidneys, etc.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
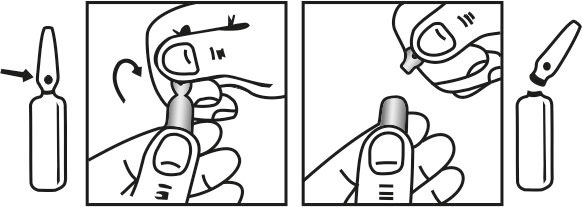
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Apply a gentle stroke. Wait for some time. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down. Being viscous solution, it takes little time to collect at the bottom. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
The daily need of Vitamin D is 400 IU on the average. In light forms of rickets the vitamin is administered in a dose of 5,000 IU daily, whereas the severe forms require an increase of the dose to 10,000 IU daily. The range between therapeutic and toxic doses is narrow.
Injections are administered intramuscularly in high doses in certain cases : e.g. 20,000 IU to breast-fed infants and 50,000 IU to children, but then the calcium blood level should be checked every week. In certain cases of rickets the so called “shock therapy” is carried out with Vitamin D2 intramuscular injection of 3,00,000 - 6,00,000 IU (active in the course of 2 months) or 5,00,000 - 10,00,000 IU for 3 - 5 days, intramuscularly. In skin and extrapulmonary tuberculosis, orchiepididymitis, laryngitis, etc., Lichen ruber planus 6,00,000 IU, three times weekly during the first week, twice weekly during the following 3 weeks, once weekly from the fifth week on to the end of the 16th week, and when necessary - 6,00,000 IU every 2 weeks till the end of one year. Dosage must be individualized under close medical supervision. Calcium intake should be adequate. Blood calcium, phosphorus and urea determinations must be made every 2 weeks, or more frequently if necessary. The bones should be x-rayed every month until the condition is corrected and stabilized.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Hypercalcemia, malabsorption syndrome, abnormal sensitivity to the toxic effects of Vitamin D, hypervitaminosis D, decreased renal function, sarcoidosis and possibly other granulomatous disease.
WARNINGS :
The effects of Vitamin D may be reduced in patients taking barbiturates or anticonvulsants. Pharmaceutical use of Vitamin D must only be undertaken under medical supervision. Concomitant use of thiazides and pharmacologic doses of Vitamin D may cause hypercalcaemia in some.
Usage in Pregnancy : Pregnancy category C :
Problems in humans have not been documented with intake of normal daily requirements. Maternal hypercalcaemia during pregnancy in humans may be associated with increased sensitivity to effects of Vitamin D, suppression of parathyroid function, or a syndrome of peculiar (elfin) facies, mental retardation and congenital aortic stenosis in infants. Hypercalcaemia during pregnancy may produce congenital disorders in the off-spring and neonatal hypoparathyroidism. Overdosage of Vitamin D has been associated with foetal abnormalities in animals.
Usage in Lactation :
Only small amounts of Vitamin D metabolites appear in human milk. Infants who are totally breast-fed and have little exposure to the sun may require Vitamin D supplementation. Vitamin D should not be administered to patients with hypercalcaemia. It should be administered with caution to infants as they may have increased sensitivity to its effects and should be used with care in patients with renal impairment or calculi, or heart disease, who might be at increased risk of organ damage if hypercalcaemia occurred. It is advised that, if possible, women receiving pharmacological doses of Vitamin D do not breast feed their infants as this may lead to the development of hypercalcaemia in the infant.
Children :
Paediatric doses must be individualized and monitored under close medical supervision.
INTERACTIONS :
Antacids, anticonvulsants, sucralfate and mineral oils reduce the effect of Vitamin D2, as they decrease.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Note : Ingestion of excessive doses of Vitamin D either as an acute overdose or over prolonged periods can result in severe toxicity. Chronic Vitamin D-induced hypercalcaemia may result in generalised vascular calcification, nephrocalcinosis, and other soft tissue calcification that may lead to hypertension and renal failure. These effects are more likely to occur when the hypercalcaemia is accompanied by hyperphosphataemia. Growth may be arrested in children, especially after prolonged administration. Death may occur as a result of renal or cardiovascular failure caused by vitamin D toxicity. The toxic doses for adults amount to 1,00,000 IU daily, taken for months, in children they are between 20,000 IU and 40,000 IU daily, also after a long-term intake.
OVERDOSAGES AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Vitamin D is the most likely of all vitamins to cause overt toxicity. Infants and children are generally more susceptible to its toxic effects. Excessive intake of Vitamin D leads to the development of hypercalcaemia and its associated effects including hypercalciuria, ectopic calcification, and renal and cardiovascular damage.
Hypervitaminosis D is characterized by :
Hypercalcaemia with anorexia, nausea, weakness, weight loss, vague aches and stiffness, constipation, diarrhoea, convulsions, mental retardation, anaemia, mild acidosis. Impairment of renal function with polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia, hypercalcuria, reversible azotaemia, hypertension, nephrocalcinosis, generalized vascular calcification, irreversible renal insufficiency, albuminuria, or urinary casts. Widespread calcification of the soft tissues, including the heart, blood vessels, renal tubules, and lungs. Bone demineralization (osteoporosis) in adults occurs concomitantly. Decline in the average rate of linear growth and increased mineralization of bones in infants and children (dwarfism).
Recommended treatment includes the following :
Hypervitaminosis D is treated by withdrawal of the vitamins, low-calcium diet, and generous fluid intake. If hypercalcaemia persists, a low-calcium diet and prednisone may be started. Severe hypercalcaemia may be treated with calcitonin, etidronate, pamidronate or gallium nitrate. Hypercalcaemic crisis requires vigorous hydration with intravenous saline to increase calcium excretion, with or without a loop diuretic. Other reported therapeutic measures include dialysis or the administration of citrates, sulfates, phosphates, corticosteroids or EDTA. Cardiac arrhythmias may be treated with small doses of potassium with continuous cardiac monitoring. Therapy may be reinstituted at a lower dose when serum calcium concentrations return to normal. Serum or urinary calcium levels should be obtained twice weekly after dosage changes.
STORAGE :
Store below 25oC, protected from light.
Do not refrigerate.
Note : Store in a place protected from direct sunlight.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
ERGOCALCIFEROL INJECTION is supplied as 2,00,000 IU (5 mg) of Ergocalciferol B.P. in 1 ml Ampoule.
Such 10 ampoules of 1 ml are packed in a Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular