5 mg/ml, 2 ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
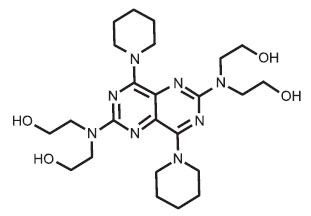
DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP (Dipyridamole) is coronary vasodilator. Chemically, Dipyridamole is Ethanol,(2,2’,2’’,2’’’-[4,8-di-1-piperidinylpyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine-2,6-diyldinitrilo] tetrakis-. The molecular formula is C24H40N8O4 and molecular weight is 504.63.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP is a sterile, clear, pale yellow solution filled in suitable size ampoule.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Dipyridamole USP 5 mg
Water for Injection USP q.s.
Contains no preservatives
ACTIONS :
Dipyridamole is a coronary vasodilator in man. The mechanism of vasodilation has not been fully elucidated, but may result from inhibition of uptake of adenosine, an important mediator of coronary vasodilation. The vasodilatory effects of dipyridamole are abolished by administration of the adenosine receptor antagonist theophylline. How dipyridamole-induced vasodilation leads to abnormalities in thallium distribution and ventricular function is also uncertain but presumably represents a “steal” phenomenon in which relatively intact vessel dilate, and sustain enhanced flow, leaving reduced pressure and flow across areas of haemodynamically important coronary vascular constriction.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Following intravenous administration, the distribution half-life in man is about 25 minutes. When plasma levels of drug are followed for up to 60 hours after i.v., plasma levels decline tri exponentially with half-lives of 5 minutes (i.v. only), 53 minutes and about 10 - 12 hours. The volume of distribution is about 140 litres with about 92 – 99 % binding to plasma proteins, primarily alpha1-acid glycoprotein.
INDICATIONS :
DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP is a coronary vasodilator & is indicated as an alternative to exercise in thallium myocardial perfusion imaging for the evaluation of coronary artery disease in patients who cannot exercise adequately. In a study of about 1100 patients who underwent coronary arteriography and DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP assisted thallium imaging, the results of both tests were interpreted blindly and the sensitivity and specificity of the Dipyridamole thallium study in predicting the angiographic outcome were calculated. The sensitivity of the Dipyridamole test (true positive Dipyridamole divided by the total number of patients with positive angiography) was about 85 %. The specificity (true negative divided by the number of patients with negative angiograms) was about 50 %. In a subset of patients who had exercise thallium imaging as well as Dipyridamole thallium imaging, sensitivity and specificity of the two tests was almost identical.
Administration :
DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP is for I.V. use only.
Prior to intravenous administration, DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP should be diluted in at least a 1:2 ratio with 0.45 % sodium chloride injection, 0.9 % sodium chloride injection, or 5 % dextrose injection for a total volume of approximately 20 to 50 ml. Infusion of undiluted DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP may cause local irritation. Diluted injection must be used immediately after dilution. Imaging agent should be injected within 5 minutes following the 4-minute infusion of DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP. Do not mix DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP with other drugs in the same syringe or infusion container.
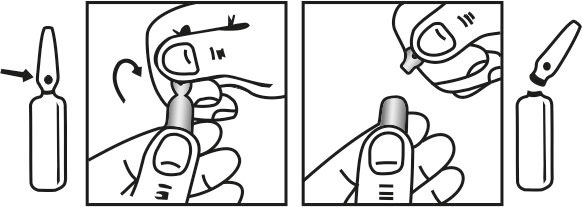
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Dosage :
The dose of intravenous dipyridamole as an adjunct to myocardial perfusion imaging should be adjusted according to the weight of the patient. The recommended dose is 0.142 mg/kg/minute (0.57 mg/kg total) infused over 4 minutes. Although the maximum tolerated dose has not been determined, clinical experience suggests that a total dose beyond 60 mg is not needed for any patient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Hypersensitivity to dipyridamole. Intravenous administration of dipyridamole is not recommended in states of shock or collapse.
WARNINGS :
Rare serious adverse reactions associated with the administration of intravenous dipyridamole for myocardial imaging have been reported. These have included fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, symptomatic ventricular tachycardia, stroke and transient cerebral ischemia. Since excessive doses of dipyridamole or intravenous doses given too rapidly can produce peripheral vasodilation, dipyridamole should be used with caution in patients with hypotension, rapidly worsening angina, subvalvular aortic stenosis or haemodynamic instability. In rare cases, such patients may be at risk for developing myocardial ischemia and infarction. An intravenous bolus of dipyridamole (40 - 50 mg over 4 minutes) can result in chest pain in patients with coronary artery disease. Rarely, hypotension or ventricular arrhythmias occur with a rapid i.v. bolus. The infusion rate should be monitored to minimize this risk. The symptoms can generally be reversed with an intravenous injection of 50 - 250 mg of aminophylline over several minutes. Patients with a history or presence of bronchial hyperreactivity may be at risk of developing bronchospasm during the use of intravenous dipyridamole as an adjunct to myocardial perfusion imaging. Although the actual overall incidence of this occurrence is small (~0.2 %), the clinical information to be gained through the use of intravenous dipyridamole should be weighed against the potential risk to the patient.
PRECAUTIONS :
Intravenous dipyridamole as an adjunct to myocardial perfusion imaging should be used with caution in patients with unstable angina, as such patients may be at risk for severe myocardial infarction. As with exercise-induced stress, the use of intravenous dipyridamole as an adjunct to myocardial perfusion imaging may occasionally precipitate cardiac arrhythmias in patients with severe heart disease. Scanning should therefore be performed with constant monitoring of the patient’s ECG. Parenteral aminophylline should be readily available and should be administered as a slow intravenous injection of 50-250 mg in the event of occurrences such as chest pain, bronchospasm, severe nausea/vomiting, hypotension, severe headache.
In the case of severe hypotension, the patient should be placed in a supine position with the head tilted down if necessary, before administration of parenteral aminophylline. If 250 mg of aminophylline does not relieve chest pain symptoms within a few minutes, sublingual nitro glycerin may be administered. If chest pain continues despite use of aminophylline and nitroglycerin, the possibility of myocardial infarction should be considered. If the clinical condition of a patient with an adverse event permits a one minute delay in the administration of parenteral aminophylline, thallium-201 may be injected and allowed to circulate for one minute before the injection of aminophylline. This will allow initial thallium perfusion imaging to be performed before reversal of the pharmacologic effects of dipyridamole on the coronary circulation.
Pregnancy : Category B.
Reproductive studies have been performed in mice, rats, and rabbits at doses of up to 125 mg/kg and have not revealed evidence of impaired embryonic development attributable to dipyridamole. However, there have not been adequate, well controlled studies in pregnant women and the drug should be used during pregnancy only if the expected benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Nursing Mothers :
Dipyridamole is excreted in human milk. Caution should therefore be used when this drug is administered to nursing mothers.
Paediatric use :
The safety and effectiveness of dipyridamole have not been established in the paediatric population.
Geriatrics :
Studies of the efficacy of single doses of intravenous Dipyridamole for myocardial perfusion imaging revealed no differences in the incidence of chest pain, ST segment depression, or severe ischemia in patients 70 years of age or older compared with patients younger than 70 years of age. Studies on the relationship of age to the effects of Dipyridamole in geriatric patients receiving the medication as a platelet aggregation inhibitor have not been done. However, no geriatrics-specific problems have been documented to date with chronic oral administration of Dipyridamole.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Aspirin :
There is evidence that the effects of aspirin and dipyridamole on platelet behaviour are additive.
Dipyridamole may increase the hypotensive effect of drugs which reduce blood pressure.
Dipyridamole may counteract the anticholinesterase effect of cholinesterase inhibitors thereby potentially aggravating myasthenia gravis.
Serious adverse events (fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, severe ventricular arrhythmias, and serious CNS abnormalities) associated with the intravenous administration of dipyridamole for myocardial imaging are described in WARNINGS. When intravenous dipyridamole was used as an adjunct to myocardial perfusion imaging in a study of 3911 patients, the following events occurred in greater than 1 % of the patients :
| Event Description |
Incidence (%) of Drug-Related Adverse Events |
| Chest Pain / angina pectoris | 19.7 |
| Headache | 12.2 |
| Dizziness | 11.8 |
| Elctrocardiographic Abnormalties / ST-T Changes | 7.5 |
| Elctrocardiographic Abnormalties / Extrasystolets | 5.2 |
| Hypotension | 4.6 |
| Nausea | 4.6 |
| Flushing | 3.4 |
| Elctrocardiographic Abnormalties / Tachycardia | 3.2 |
| Dyspnoea | 2.6 |
| Pain Unspecified | 2.6 |
| Blood Pressure Lability | 1.6 |
| Hypertension | 1.5 |
| Paresthesia | 1.3 |
| Fatigue | 1.2 |
Less common events (i.e., occurred in 1 % or less of the patients in the study) included, in decreasing order of frequency :
Cardiovascular System :
Electrocardiographic abnormalities unspecified, arrhythmia unspecified, palpitation, ventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, myocardial infarction, AV block, syncope, orthostatic hypotension, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmia unspecified, heart block unspecified, cardiomyopathy, oedema.
Gastrointestinal System :
Dyspepsia, dry mouth, abdominal pain, flatulence,vomiting, eructation, dysphagia, tenesmus, increased appetite.
Pharyngitis, bronchospasm, hyperventilation, rhinitis, coughing, pleural pain.
Myalgia, back pain, injection site reaction unspecified, diaphoresis, asthenia, malaise, arthralgia, injection site pain, rigor, earache, tinnitus, vision abnormalities unspecified, dysgeusia, thirst, depersonalization, eye pain, renal pain, perineal pain, breast pain, intermittent claudication, leg cramping.
Symptoms such as warm feeling, flushes, sweating, restlessness, feeling of weakness, dizziness and angina complaints can be experience. A drop in blood prove and tachycardia may be observed.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Administration of xanthin derivatives (e.g aminophyline) may reverse the haemodynamic effect of dipyridamole overdosage.
Store between 30°C (86°F), protected from light. Do not Freeze.
24 months from the date of manufacture.
DIPYRIDAMOLE INJECTION USP is supplied as 10 mg of dipyridamole USP in 2 ml ampoule.
5 Ampoules per Box.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular