50 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
Procarbazine hydrochloride, is a hydrazine derivative antineoplastic agent. Chemically, procarbazine hydrochloride is N-Isopropyl-α-(2-methylhydrazino)-ptoluamide monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C12H19N3O·HCl and molecular weight is 257.76.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
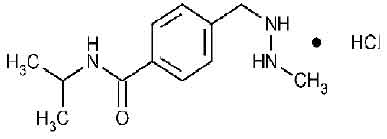
PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is a hard gelatin opaque ivory capsule.
COMPOSITION :
Each hard gelatin capsule contains :
Procarbazine Hydrochloride USP
equivalent to Procarbazine 50 mg
Excipients q.s.
Approved colours used in empty capsule shells.
ACTIONS :
The precise mode of cytotoxic action of procarbazine has not been clearly defined. There is evidence that the drug may act by inhibition of protein, RNA and DNA synthesis. Studies have suggested that procarbazine may inhibit transmethylation of methyl groups of methionine into t-RNA. The absence of functional t-RNA could cause the cessation of protein synthesis and consequently DNA and RNA synthesis. In addition, procarbazine may directly damage DNA. Hydrogen peroxide, formed during the auto-oxidation of the drug, may
attack protein sulfhydryl groups contained in residual protein which is tightly bound to DNA.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Procarbazine is rapidly and completely absorbed. Following oral administration of 30 mg of 14C-labeled procarbazine, maximum peak plasma radioactive concentrations were reached within 60 minutes. After intravenous injection, the plasma half-life of procarbazine is approximately 10 minutes. Approximately 70 % of the radioactivity is excreted in the urine as N-isopropylterephthalamic acid within 24 hours following both oral and intravenous administration of 14C-labeled procarbazine. Procarbazine crosses the blood-brain barrier and rapidly equilibrates between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid after oral administration. Procarbazine is metabolized primarily in the liver and kidneys. The drug appears to be auto-oxidized to the azo derivative with the release of hydrogen peroxide. The azo derivative
isomerizes to the hydrazone, and following hydrolysis splits into a benzylaldehyde derivative and methylhydrazine. The methylhydrazine is further degraded to CO2 and CH4 and possibly hydrazine, whereas the aldehyde is oxidized to N-isopropylterephthalamic acid, which is excreted in the urine.
INDICATIONS :
PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is indicated for use in combination with other anticancer drugs for the treatment of Stage III and IV Hodgkin’s disease. PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is used as part of the MOPP (nitrogen mustard, vincristine, procarbazine, prednisone) regimen. PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES may also be useful in other advanced lymphomata and a variety of solid tumours which have proved resistant to other forms of therapy.
Administration :
PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES are for oral administration.
Dosage :
The following doses are for administration of the drug as a single agent. When used in combination with other anticancer drugs, PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES dose should be appropriately reduced, e.g. in the MOPP regimen, the PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES dose is 100 mg/m2 daily for 14 days. All dosages are based on the patient’s actual weight. However, the estimated lean body mass (dry weight) is used if the patient is obese or if there has been a spurious weight gain due to oedema, ascites or other forms of abnormal fluid retention.
Adults :
To minimize the nausea and vomiting experienced by a high percentage of patients beginning PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES therapy, single or divided doses of 2 to 4 mg/kg/day for the first week are recommended. Daily dosage should then be maintained at 4 to 6 mg/kg/day until maximum response is obtained or until the white blood count falls below 4000/cmm or the platelets fall below 100,000/cmm. When maximum response is obtained, the dose may be maintained at 1 to 2 mg/kg/day. Upon evidence of haematologic or other toxicity the drug should be discontinued until there has been satisfactory recovery. After toxic side effects have subsided, therapy may then be resumed at the discretion of the physician, based on clinical evaluation and appropriate laboratory studies, at a dosage of 1 to 2 mg/kg/day.
Paediatric Patients :
Very close clinical monitoring is mandatory. Undue toxicity, evidenced by tremors, coma and convulsions, has occurred in a few cases. Dosage, therefore, should be individualized. The following dosage schedule is provided as a guideline only. Fifty (50) mg per square meter of body surface per day is recommended for the first week. Dosage should then be maintained at 100 mg per square meter of body surface per day until maximum response is obtained or until leucopenia or thrombocytopenia occurs. When maximum response is attained, the dose may be maintained at 50 mg per square meter of body surface per day. Upon evidence of haematologic or other toxicity, the drug should be discontinued until there has been satisfactory recovery, based on clinical evaluation and appropriate laboratory
tests. After toxic side effects have subsided, therapy may then be resumed.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or inadequate marrow reserve as demonstrated by bone marrow aspiration. Due consideration of this possible state should be given to each patient who has leucopenia, thrombocytopenia or anaemia.
WARNINGS :
To minimize CNS depression and possible potentiation, barbiturates, antihistamines, narcotics, hypotensive agents or phenothiazines should be used with caution. Ethyl alcohol should not be used since there may be an Antabuse (disulfiram)-like reaction. Because PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES exhibits some monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity, sympathomimetic drugs, tricyclic antidepressant drugs (e.g. amitriptyline HCI, imipramine HCI) and other drugs and foods with known high tyramine content, such as wine, yogurt, ripe cheese and bananas, should be avoided. A further phenomenon of toxicity common to many hydrazine derivatives is haemolysis and the appearance of Heinz-Ehrlich inclusion bodies in erythrocytes.
Pregnancy :
Teratogenic Effects : Pregnancy Category D. Procarbazine hydrochloride can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. While there are no adequate and well-controlled studies with procarbazine hydrochloride in pregnant women, there are case reports of malformations in the offspring of women who were exposed to procarbazine hydrochloride in combination with other antineoplastic agents during pregnancy. PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the foetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised
to avoid becoming pregnant. Procarbazine hydrochloride is teratogenic in the rat when given at doses approximately 4 to 13 times the maximum recommended human therapeutic dose of 6 mg/kg/day.
Nonteratogenic Effects :
Procarbazine hydrochloride has not been adequately studied in animals for its effects on peri- and postnatal development. However, neurogenic tumors were noted in the offspring of rats given intravenous injections of 125 mg/kg of procarbazine hydrochloride on day
22 of gestation. Compounds which inhibit DNA, RNA and protein synthesis might be expected to have adverse effects on peri- and postnatal development.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for procarbazine hydrochloride in animal studies, mothers should not nurse while receiving this drug.
Paediatric Use :
Undue toxicity, evidenced by tremors, coma and convulsions, has occurred in a few cases. Dosage, therefore, should be individualized. Very close clinical monitoring is mandatory.
PRECAUTIONS :
General :
Undue toxicity may occur if PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES is used in patients with impairment of renal and/or hepatic function. When appropriate, hospitalization for the initial course of treatment should be considered. If radiation or a chemotherapeutic agent known to have marrow-depressant activity has been used, an interval of one month or longer without such therapy is recommended before starting treatment with PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES. The length of this interval may also be determined by evidence of bone marrow recovery based on successive bone marrow studies. Prompt cessation of therapy is recommended if any one of the following occurs :
Central nervous system signs or symptoms such as paresthesias, neuropathies or confusion.
Leucopenia (white blood count under 4000).
Thrombocytopenia (platelets under 100,000).
Hypersensitivity reaction.
Stomatitis : The first small ulceration or persistent spot soreness around the oral cavity is a signal for cessation of therapy.
Diarrhoea : Frequent bowel movements or watery stools. Haemorrhage or bleeding tendencies. Bone marrow depression often occurs 2 to 8 weeks after the start of treatment. If leucopenia occurs, hospitalization of the patient may be needed for appropriate treatment to prevent systemic infection.
CARCINOGENESIS :
The carcinogenicity of procarbazine hydrochloride in mice, rats and monkeys has been reported in a considerable number of studies. Instances of a second nonlymphoid malignancy, including lung cancer and acute myelocytic leukemia, have been reported in patients with Hodgkin’s disease treated with procarbazine in combination with other chemotherapy and/or radiation. The risks of secondary lung cancer from treatment appear to be multiplied by tobacco use. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) considers that
there is “sufficient evidence” for the human carcinogenicity of procarbazine hydrochloride when it is given in intensive regimens which include other antineoplastic agents but that there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans given procarbazine hydrochloride alone.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Patients should be warned not to drink alcoholic beverages while on PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES therapy since there may be an Antabuse (disulfiram)-like reaction. They should also be cautioned to avoid foods with known high tyramine content such as wine, yogurt, ripe cheese and bananas. Over-the-counter drug preparations which contain antihistamines or sympathomimetic drugs should also be avoided. Patients taking PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES should also be warned against the use of prescription drugs without the knowledge and consent of their physician. Patients should be advised to discontinue tobacco use.
Laboratory Tests :
Baseline laboratory data should be obtained prior to initiation of therapy. The haematologic status as indicated by haemoglobin, haematocrit, white blood count (WBC), differential, reticulocytes and platelets should be monitored closely - at least every 3 or 4 days. Hepatic and renal evaluation are indicated prior to beginning therapy. Urinalysis, transaminase, alkaline phosphatase and blood urea nitrogen tests should be repeated at least weekly.
DRUG INTERACTIONS :
No cross-resistance with other chemotherapeutic agents, radiotherapy or steroids has been demonstrated.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Leucopenia, anaemia and thrombopenia occur frequently. Nausea and vomiting are the most commonly reported side effects.
OVERDOSAGE :
The major manifestations of overdosage with PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES would be anticipated to be nausea, vomiting, enteritis, diarrhoea, hypotension, tremors, convulsions and coma. The estimated mean lethal dose of procarbazine
hydrochloride in laboratory animals varied from approximately 150 mg/kg in rabbits to 1300 mg/kg in mice.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Treatment should consist of either the administration of an emetic or gastric lavage. General supportive measures such as intravenous fluids are advised. Since the major toxicity of procarbazine hydrochloride is haematologic and hepatic, patients should have frequent complete blood counts and liver function tests throughout their period of recovery and for a minimum of two weeks thereafter. Should abnormalities appear in any of these determinations, appropriate measures for correction and stabilization should be immediately undertaken.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C, protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
PROCARBAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE CAPSULES contains equivalent of 50 mg procarbazine.
5 strips of 10 capsules in a box .
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular