5 mg/10 ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
CARDATEN (Atenolol) a synthetic, beta1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent, may be chemically described as benzeneacetamide, 4-[2-hydroxy-3-[(1-methylethyl)amino]propoxy]-. The molecular formula is C14H22N2O3. Atenolol (free base) has a molecular weight of 266.34.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
-structure.jpg)
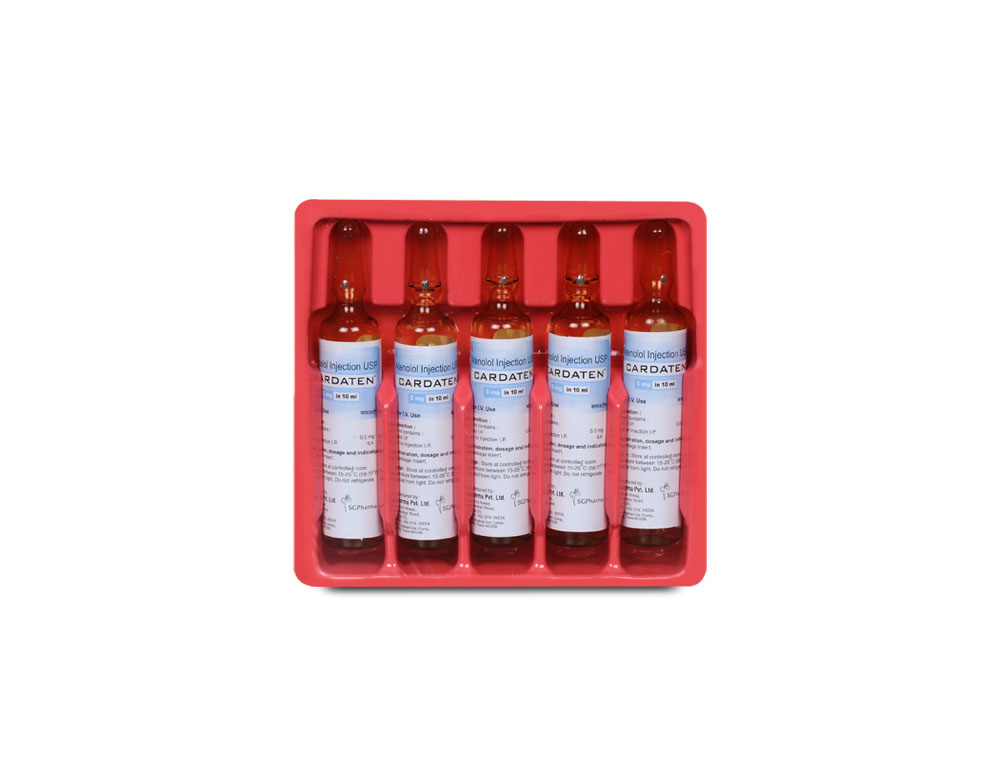
A clear colourless solution filled in 10 ml amber ampoule.
ACTIONS :
CARDATEN is a beta1-selective (cardioselective) beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agent without membrane stabilizing or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activities. This preferential effect is not absolute, however, and at higher doses, CARDATEN inhibits beta2-adrenoreceptors, chiefly located in the bronchial and vascular musculature.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
In man, absorption of an oral dose is rapid and consistent but incomplete. Approximately 50 % of an oral dose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, the remainder being excreted unchanged in the faeces. Peak blood levels are reached between two and four hours after ingestion. Unlike Propranolol or Metoprolol, but like Nadolol, CARDATEN undergoes little or no metabolism by the liver and the absorbed portion is eliminated primarily by renal excretion. Over 85 % of an intravenous dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours compared with approximately 50 % for an oral dose. CARDATEN also differs from Propranolol in that only a small amount (6 % - 16 %) of Atenolol is bound to proteins in the plasma. This kinetic profile results in relatively consistent plasma drug levels with about a fourfold interpatient variation. The elimination half-life of oral CARDATEN is approximately 6 to 7 hours and there is no alteration of the kinetic profile of the drug by chronic administration. Following intravenous administration, peak plasma levels are reached within 5 minutes. Declines from peak levels are rapid (5 to 10 fold) during the first 7 hours; thereafter, plasma levels decay with a half-life similar to that of orally administered drug. Following oral doses of 50 mg or 100 mg, both beta-blocking and antihypertensive effects persist for at least 24 hours. When renal function is impaired, elimination of CARDATEN is closely related to the glomerular filtration rate; significant accumulation occurs when the creatinine clearance falls below 35 mL/min/1.73m2.
Elderly patients present higher Atenolol plasma levels with total clearance values about 50 % lower than younger subjects. The half life is markedly longer in elderly compare to younger subjects.
Arrhythmias :
CARDATEN is indicated in the management of arrhythmias. For the early intervention treatment of Acute
CARDATEN Injection is administered by the intravenous route.
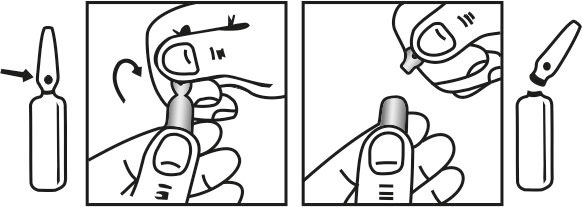
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C. (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Adults :
Arrhythmias :
A suitable initial dose of CARDATEN Injection is 2.5 mg (5 ml) injected intravenously over a 2.5 minute period (i.e. 1 mg/minute). This may be repeated at 5 minutes intervals until a response is observed upto a maximum dosage of 10 mg. If CARDATEN Injection is given by infusion, 0.15 mg/kg body weight may be administered over a 20 minute period. If required, the injection or infusion may be repeated every 12 hours. Having controlled the arrhythmias with IV CARDATEN, a suitable oral maintenance dosage is 50 to 100 mg daily.
Acute Myocardial Infarction :
In patients with definite or suspected acute myocardial infarction, treatment with CARDATEN Injection should be initiated as soon as possible after the patients arrival in the hospital and after eligibility is established. Such treatment should be initiated in a coronary care or similar unit immediately after the patients hemodynamic condition has stabilized. Treatment should begin with the intravenous administration of 5 mg CARDATEN Injection over 5 minutes followed by another 5 mg intravenous injection 10 minutes later. CARDATEN Injection should be administered under carefully controlled conditions including monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate and electrocardiogram. Dilutions of CARDATEN Injection in Dextrose Injection USP, Sodium Chloride Injection USP, or Sodium Chloride and Dextrose Injection may be used. These admixtures are stable for 48 hours if they are not used immediately. In patients who tolerate the full intravenous dose (10 mg), Atenolol Tablets 50 mg should be initiated 10 minutes after the last intravenous dose followed by another 50 mg oral dose 12 hours later. Thereafter, Atenolol Tablets can be given orally either 100 mg once daily or 50 mg twice a day for a further 6-9 days or until discharge from the hospital. If bradycardia or hypotension requiring treatment or any other untoward effects occur, Atenolol Tablets should be discontinued.
Data from other beta blocker trials suggest that if there is any question concerning the use of IV beta blocker or clinical estimate that there is a contraindication, the IV beta blocker may be eliminated and patients fulfilling the safety criteria may be given Atenolol Tablets 50 mg twice daily or 100 mg once a day for at least seven days (if the IV dosing is excluded). Although the demonstration of efficacy of Atenolol Tablets is based entirely on data from the first seven postinfarction days, data from other beta blocker trials suggest that treatment with beta blockers that are effective in the postinfarction setting may be continued for one to three years if there are no contraindications. CARDATEN is an additional treatment to standard coronary care unit therapy.
Since Atenolol is excreted via the kidneys, dosage should be adjusted in cases of severe impairment of renal function. No significant accumulation of CARDATEN occurs until creatinine clearance falls below 35 mL/min/1.73m2 (normal range is 100 - 150 mL/min/1.73m2). For Patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 to 35 mL/min/1.73m2 (equivalent to serum creatinine of 300 to 600 micromol/litre) the oral dose should be 50 mg daily and intravenous dose should be 10 mg once every two days. For patients with creatinine clearance of < 15 mL/min/1.73m2 (equivalent to serum creatinine of > 600 micromol/Litre) the oral dose should be 25 mg daily or 50 mg on alternate days and the intravenous dose should be 10 mg once every four days.
Cardiac failure :
Sympathetic stimulation is necessary in supporting circulatory function in congestive heart failure and beta blockade carries the potential hazard of further depressing myocardial contractility and precipitating more severe failure. In patients who have congestive heart failure controlled by digitalis and/or diuretics, CARDATEN should be administered cautiously. Both digitalis and Atenolol slow AV conduction. In patients with acute myocardial infarction, cardiac failure which is not promptly and effectively controlled by 80 mg of intravenous furosemide or equivalent therapy is a contraindication to beta-blocker treatment.
Thyrotoxicosis :
Beta-adrenergic blockade may mask certain clinical signs (e.g. tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of having thyroid disease should be monitored closely when administering CARDATEN Injection. Abrupt withdrawal of beta blockade might precipitate a thyroid storm; therefore, patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis from whom CARDATEN therapy is to be withdrawn should be monitored closely.
Pregnancy Category D :
CARDATEN can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. CARDATEN crosses the placental barrier and appears in cord blood. Administration of CARDATEN, starting in the second trimester of pregnancy, has been associated with the birth of infants that are small for gestational age. No studies have been performed on the use of CARDATEN in the first trimester and the possibility of foetal injury cannot be excluded. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the foetus.
CARDATEN is excreted in human breast milk at a ratio of 1.5 to 6.8 when compared to the concentration in plasma. Caution should be exercised when CARDATEN is administered to a nursing woman. Clinically significant bradycardia has been reported in breast fed infants. Premature infants, or infants with impaired renal function may be more likely to develop adverse effects.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Catecholamine-depleting drugs (e.g. Reserpine) may have an additive effect when given with beta-blocking agents. Patients treated with CARDATEN plus a catecholamine depletor should therefore be closely observed for evidence of hypotension and/or marked bradycardia which may produce vertigo, syncope or postural hypotension. Calcium channel blockers may also have an additive effect when given with CARDATEN. Beta blockers may exacerbate the rebound hypertension which can follow the withdrawal of clonidine. If the two drugs are co administered, the beta blocker should be withdrawn several days before the gradual withdrawal of clonidine. If replacing clonidine by beta-blocker therapy, the introduction of beta blockers should be delayed for several days after clonidine administration has stopped.
Most adverse effects have been mild and transient. Cardio Vascular : Bradycardia, heart failure deterioration, postural hypotension which may be associated with syncope, cold extremities. In susceptible patients : precipitation of heart block, intermittent claudication, Raynauds phenomenon.
Hematologic : Agranulocytosis, purpura, thrombo-cytopenia.
Other : Erythematous rash, fatigue.
Miscellaneous :
There have been reports of skin rashes and/or dry eyes associated with the use of beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. The reported incidence is small, and in most cases, the symptoms have cleared when treatment was withdrawn. Discontinuance of the drug should be considered if any such reaction is not otherwise explicable. Patients should be closely monitored following cessation of therapy. The oculomucocutaneous syndrome associated with the beta blocker practolol has not been reported with CARDATEN. Furthermore, a number of patients who had previously demonstrated established practolol reactions were transferred to CARDATEN therapy with subsequent resolution or quiescence of the reaction. In addition, a variety of adverse effects have been reported with other beta-adrenergic blocking agents and may be considered potential adverse effects of CARDATEN.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Treatment of overdose should be directed to the removal of any unabsorbed drug by induced emesis, gastric lavage, or administration of activated charcoal. CARDATEN can be removed from the general circulation by hemodialysis. Other treatment modalities should be employed at the physicians discretion and may include :
STORAGE :
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular